In today’s
fast-evolving tech world, software teams must ship faster, test smarter, and
automate every possible step of their development pipelines. That’s where Jenkins DevOps comes in. Whether you
are a startup or a full-scale Software
Development Company, integrating Jenkins can be a game-changer.
He, she,
or any tech enthusiast working in development or quality assurance has likely
heard of Jenkins. But how does it actually work? And how can it fit into your
business needs, especially if you're focusing on Test Automation Services?
Let’s
break it all down in this user-friendly guide designed specifically for teams
looking to streamline DevOps.
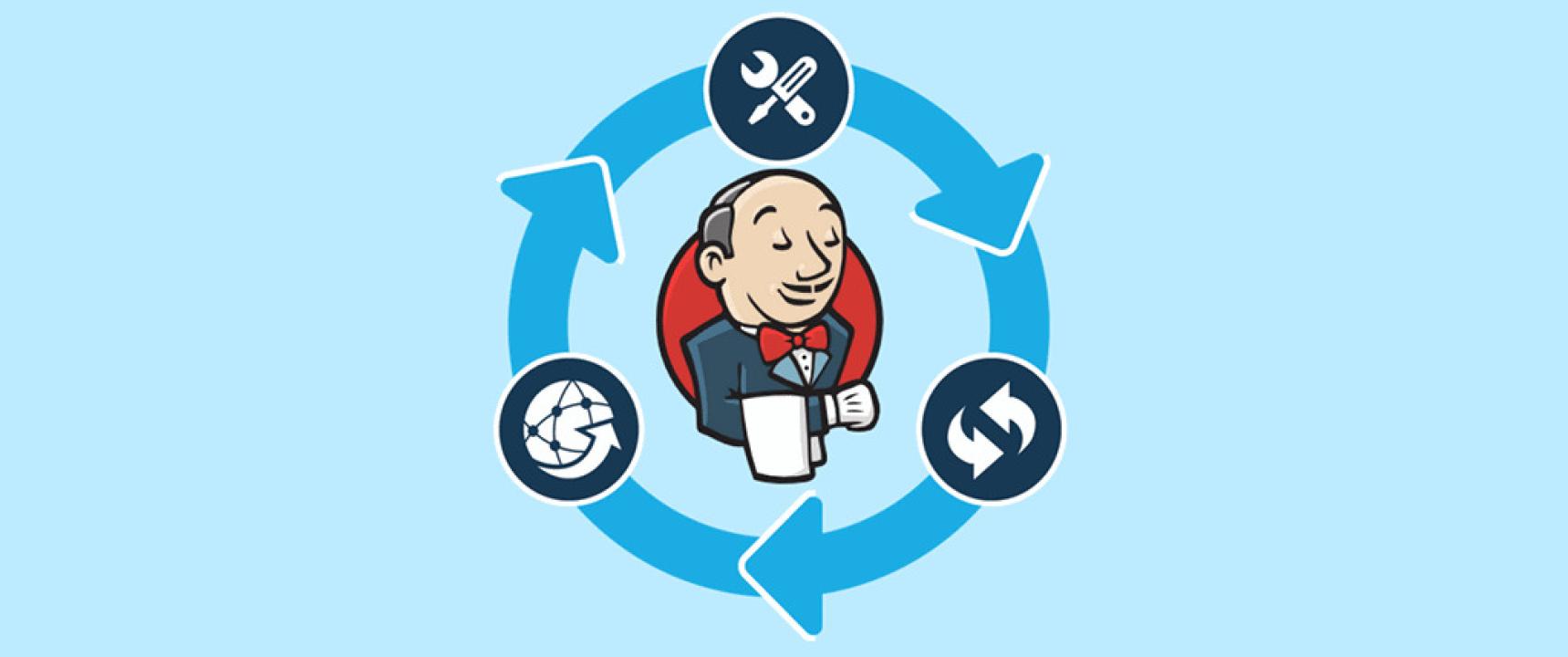
What Is Jenkins?
Jenkins is an open-source automation server that
simplifies building, testing, and deploying software. It helps developers
integrate changes to a project more frequently by using Continuous Integration
(CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) practices.
He or she
using Jenkins can automate repetitive tasks, trigger test cases, and ensure
reliable delivery pipelines. Thanks to its extensibility and a vast ecosystem
of plugins, Jenkins works across multiple environments, including Docker,
Kubernetes, AWS, and more.
Jenkins in DevOps
The role
of Jenkins in DevOps is
central. DevOps is about collaboration between development and operations, and
Jenkins is the tool that connects them. It allows teams to:
- Build code continuously
- Run automated tests
- Detect issues early
- Deploy changes rapidly
This
results in faster delivery cycles and fewer bugs in production.
How Does Jenkins DevOps Work?
Let’s
look at a simplified flow of how Jenkins
DevOps operates in real-time:
Step 1: Code Commit
A
developer commits code to the version control system like Git. Jenkins detects
the change and starts the pipeline automatically.
Step 2: Build
Jenkins
fetches the latest code and builds it into an executable format (e.g., a JAR
file). If the build fails, Jenkins notifies the team immediately.
Step 3: Testing
Next,
automated tests run to validate functionality. This stage plays a vital role in
Test Automation Services, as
Jenkins can integrate with tools like Selenium, JUnit, or TestNG.
Step 4: Deployment
Once
tests pass, Jenkins deploys the build to a staging or production environment.
This ensures that only tested and validated code goes live.
Step 5: Monitoring & Feedback
Jenkins
provides detailed reports and logs. Teams can review the results, fix issues,
and repeat the process.
Why Should a Software Development Company Use Jenkins?
A Software
Development Company looking to stay agile and competitive must adopt
CI/CD practices. Here’s why Jenkins fits like a glove:
1. Supports Continuous Delivery
Jenkins
helps teams deliver code updates regularly and reliably. This makes your
development cycles lean and quick.
2. Test Automation Integration
For teams
offering Test Automation Services,
Jenkins is a perfect hub. It triggers and manages automated tests, tracks
performance, and sends alerts.
3. Wide Plugin Support
Jenkins
has over 1,800 plugins. He or she can integrate it with tools like GitHub,
Docker, Ansible, JIRA, and more.
4. Scalable Architecture
Jenkins
supports master-slave architecture, enabling large teams to run parallel builds
and reduce wait times.
5. Cost-Efficient
As an
open-source tool, Jenkins minimizes software costs, especially for startups or
businesses in India trying to build quality with budget constraints.
How Can I Use Jenkins for My Business?
Whether
you’re running a freelance dev team or managing a large Software Development Company, Jenkins fits most business models.
Here’s how you can implement it:
Set Up Jenkins Server
Install
Jenkins on your local server or cloud platform. Configure the necessary
environment variables and dependencies.
Connect Your Version Control
Link
Jenkins to Git, GitHub, Bitbucket, or any other SCM tool. Every time code
changes, Jenkins gets notified.
Create a Pipeline
Design a
pipeline to define your build, test, and deploy stages. Jenkins’
Pipeline-as-Code (using Jenkinsfile) makes this super manageable.
Automate Testing
Integrate
Jenkins with your Test Automation
Services. Add test steps for every build to validate functionality
before deployment.
Monitor and Iterate
Check
Jenkins dashboards for logs, errors, and history. Use this data to fine-tune
your processes.
Key Benefits of Using Jenkins DevOps
Let’s
summarize why Jenkins DevOps continues to dominate the CI/CD landscape:
Early Bug Detection
With
Jenkins running your tests after every commit, teams detect and fix bugs
earlier.
Rapid Releases
Frequent
and reliable delivery becomes standard practice.
Better Team Collaboration
DevOps
promotes shared responsibility, and Jenkins is the bridge between teams.
Enhanced Test Automation
It
supports all popular tools for automation testing, a core feature of modern Test Automation Services.
Strong Ecosystem
Whatever
tool your team uses—chances are, Jenkins already integrates with it.
Key Takeaways
- Jenkins
DevOps
enables Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery, streamlining
modern software development.
- It automates builds, tests,
and deployments, reducing manual work and improving accuracy.
- A Software Development Company or freelance team can use Jenkins
to enhance collaboration and efficiency.
- Its flexibility supports a
wide range of tools and is essential for teams offering Test Automation Services.
- Jenkins is open-source,
scalable, and backed by a large global community.
Conclusion
He or she
who works in the software development lifecycle understands that speed,
quality, and automation are no longer luxuries—they are requirements. Jenkins DevOps stands out as a
critical tool for bridging the gap between development and operations.
Whether
you’re a small team or a full-fledged Software
Development Company, implementing Jenkins into your workflow can
significantly improve productivity and product quality. Combine Jenkins with
powerful Test
Automation Services, and your DevOps pipeline becomes unstoppable.
Don’t
wait. Try it, experiment with it, and evolve your software strategy with
Jenkins.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Jenkins used for in DevOps?
Jenkins
is used to automate the processes of building, testing, and deploying software.
It ensures faster and more reliable delivery in a DevOps pipeline.
Can a small company use Jenkins effectively?
Yes.
Jenkins is open-source and works well for startups and mid-sized businesses.
Its plugin ecosystem allows for customization based on business size.
Does Jenkins support Test Automation?
Absolutely.
Jenkins integrates with popular testing tools like Selenium, TestNG, and JUnit,
making it ideal for teams offering Test
Automation Services.