If you’ve ever wondered why your video call lags on Wi-Fi but works well when you plug in a cable, you’re not alone. Many people find it hard to grasp the real difference between Ethernet and Wi-Fi, especially as our homes get filled with smart devices, online work, gaming, and nonstop streaming. With so many types of internet connections available today, picking the right setup can be confusing.
Let’s clear things up. In this guide, we explain Wi-Fi compared to wireless internet, examine wired versus wireless networks, and describe how each technology works. By the end, you’ll understand which connection fits your life>
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
The debate isn’t just about convenience.
It’s about:
Stability
Speed
Security
Latency
Performance under pressure
Everyday user experience
From casual browsing to important work calls, your choice between Wi-Fi and Ethernet affects how smooth your internet is. With more devices connecting than ever, understanding both options helps you create a network that is reliable and not frustrating.
What Exactly Is Wi-Fi (Wireless Internet)?
Let’s begin with the star of modern connectivity: Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that uses radio signals to connect your devices to the router. When people mention “wireless internet,” they usually mean Wi-Fi. However, wireless internet can also include:
Mobile hotspot networks
4G/5G home internet
Fixed wireless broadband
Satellite internet
Wi-Fi simply transmits your internet through the air instead of through cables.
How Wi-Fi Works
Your router sends radio waves throughout your home. Devices like laptops, phones, and smart TVs catch these signals and connect. The closer and clearer the path, the stronger the signal.
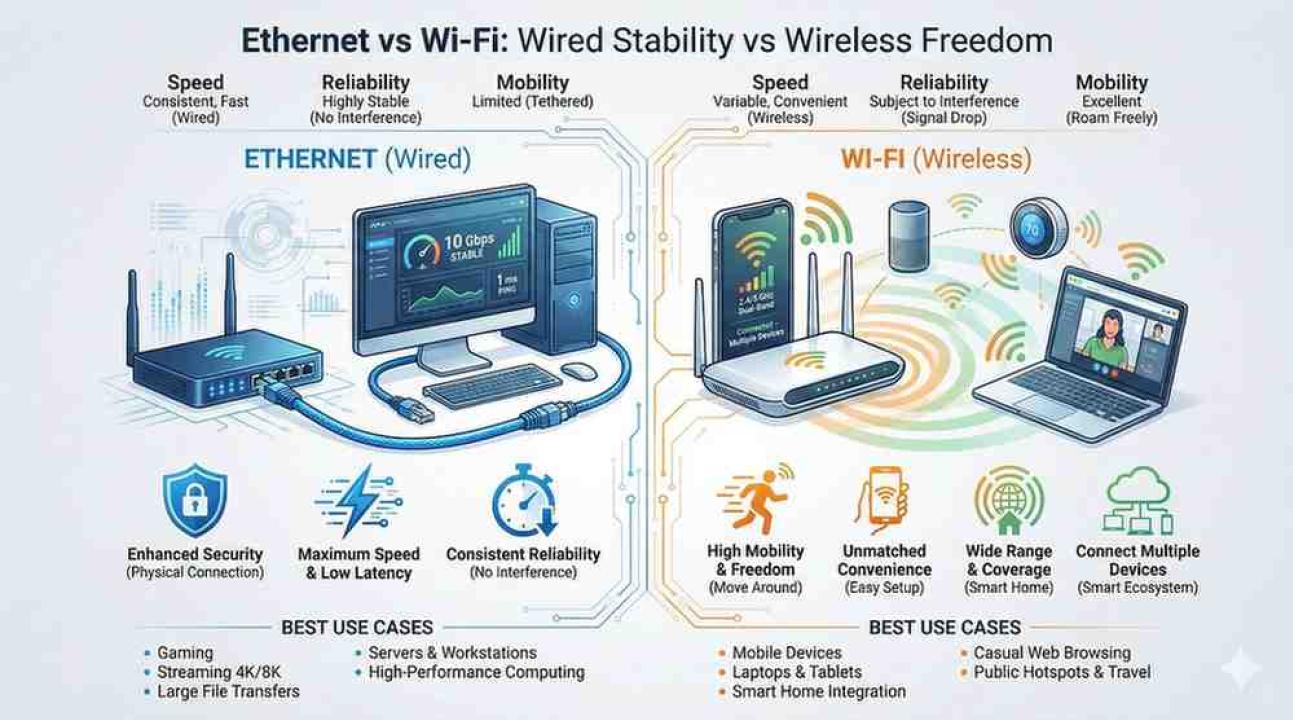
Wi-Fi Advantages
Wi-Fi wins big in areas like:
Convenience – Connect instantly without cables
Mobility – Move freely around your home
Supports many devices – Great for smart homes
Easy setup – No need to run wires through walls
Flexible placement – Works anywhere within range
Wi-Fi Disadvantages
But it also comes with drawbacks:
Signal interference (walls, microwaves, neighbors)
Slower speeds compared to wired
Higher latency
Less secure if not properly configured
Signal weakens with distance
If you’ve ever had a device drop connection for no reason, that's Wi-Fi being Wi-Fi.
What Is Ethernet (Wired Internet)?
Ethernet is the traditional wired method of accessing the internet. You connect your device directly to the router with an Ethernet cable.
How Ethernet Works
Unlike radio waves, Ethernet uses copper wires (or fiber) to deliver stable, high-speed data with almost no interference.
Ethernet Advantages
Where Wi-Fi struggles, Ethernet shines:
Ultra-stable connection
Consistent high speeds
Very low latency
More secure
Not affected by walls or interference
This is why professional gamers, streamers, and remote workers often swear by Ethernet.
Ethernet Disadvantages
Of course, it’s not perfect:
Requires cables everywhere
Not ideal for mobile devices
Setup takes more effort
Limited to areas where cables reach
If you prefer a clean, wire-free home—Ethernet may not be your aesthetic.
Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: Understanding the Core Differences
Now that we understand both, let’s compare them directly using real-world scenarios.
1. Speed: Which One Is Faster?
Most Wi-Fi routers today support fast speeds, but in real-life performance:
Wi-Fi speeds vary constantly
Ethernet speeds remain consistent and closer to your plan
For example, if you pay for 500 Mbps:
Wi-Fi might give you 200–400 Mbps depending on interference
Ethernet often reaches 480–500 Mbps consistently
Winner: Ethernet
2. Stability and Reliability
Wi-Fi can drop unpredictably due to:
Thick walls
Competing networks
Household appliances
Distance from router
Ethernet faces none of these issues.
Winner: Ethernet
3. Latency (Ping)
Latency matters for:
Gaming
Video conferencing
Remote work
Cloud applications
Wi-Fi produces fluctuations, while Ethernet provides a steady, low-ping connection.
Winner: Ethernet
4. Security
Wi-Fi can be secure, but only if:
You use strong passwords
You enable WPA3
You update router firmware
Ethernet is inherently more secure simply because someone must physically connect to your network.
Winner: Ethernet
5. Mobility and Convenience
This is where Wi-Fi shines.
You can:
Move around freely
Use smartphones, tablets, and smart devices
Connect more devices without cables
Ethernet makes you feel “tethered,” literally.
Winner: Wi-Fi
6. Multi-Device Support
Wi-Fi handles dozens of devices perfect for smart homes.
Ethernet supports only one device per cable unless you use switches.
Winner: Wi-Fi
7. Use Cases: When to Choose Which?
Choose Ethernet if:
You’re gaming
You work from home
You livestream or upload large files
You want zero lag
You use a desktop computer
You run a home office or server
Choose Wi-Fi if:
You use mobile devices
You value convenience
You don’t want messy cables
You have many smart home gadgets
You want internet everywhere in your home
Most households benefit from using both Wi-Fi for mobility, Ethernet for consistency.
Understanding Internet Connection Types
Your decision can also depend on what type of internet connections you have:
Fiber Internet – Ultra-fast, works well with both Ethernet and Wi-Fi
Cable Internet – Good speeds, best through Ethernet
DSL Internet – Slower but stable, Ethernet maximizes performance
Fixed Wireless Internet – Can fluctuate; Ethernet reduces internal network issues
Satellite Internet – High latency no matter what; Ethernet improves internal consistency
4G/5G Home Internet – Wi-Fi can fluctuate; Ethernet minimizes local issues
No matter your provider, Ethernet usually enhances performance.
Which One Should You Use?
If you need peak performance, Ethernet is hands-down better.
If you need flexibility, Wi-Fi is the obvious choice.
But the smartest setup?
A hybrid network:
Ethernet for high-priority devices (PC, smart TV, consoles)
Wi-Fi for phones, tablets, and smart gadgets
This combination delivers stability and convenience.
Conclusion
Understanding the main differences between Ethernet and Wi-Fi isn’t just tech knowledge; it affects your online experience.
Ethernet offers stability, security, and smooth performance. Wi-Fi provides freedom, convenience, and support for multiple devices.
Both have benefits, and neither is “better” for everyone. Instead, consider how you use the internet. Whether you’re streaming, gaming, working, or simply scrolling, all those experiences rely on making the right connection choice. If possible, combine both for the best of both worlds.
FAQs About Wi-Fi vs Ethernet
1. Is Ethernet faster than Wi-Fi?
Yes, Ethernet typically provides more consistent and faster speeds. With a direct cable connection, it avoids interference and signal drops that can slow down Wi-Fi. This makes it ideal for activities that require fast, reliable internet.
2. What’s the main difference between Wi-Fi and wireless internet?
Wi-Fi is a type of wireless internet provided through a router. Wireless internet can also include mobile data, fixed wireless, and satellite connections. Essentially, Wi-Fi is a subset of the broader wireless internet category.
3. Does Ethernet improve gaming performance?
Absolutely. Ethernet offers a stable, low-latency connection that lowers ping and lag. Gamers often prefer Ethernet to prevent interruptions and ensure smooth, real-time gameplay.
4. Which is safer: Ethernet or Wi-Fi?
Ethernet is generally more secure because it needs a physical connection for access. Wi-Fi, while safe with strong passwords and encryption, can be vulnerable to hacking or unauthorized access. Physical connections significantly reduce these risks.
5. Should I use both Ethernet and Wi-Fi?
Yes. Most homes benefit from a hybrid setup. Using Ethernet for crucial devices and Wi-Fi for mobile or smart devices ensures both stability and flexibility across your network.