Introduction
Imagine deploying a new feature, only to discover later that it broke something in production. Now imagine catching that bug moments after a developer commits the code all automatically. That’s the promise of integrating Selenium with Jenkins in a CI/CD pipeline.
As development teams embrace Agile and DevOps, continuous testing is essential to maintain quality at speed. Tools like Selenium and Jenkins play a central role in test automation and CI/CD integration. If you're pursuing a Selenium certification online or looking for online Selenium training, understanding this integration is crucial.
This blog dives deep into how Selenium fits into the Jenkins ecosystem to automate tests, trigger builds, and support continuous delivery. Whether you're a beginner exploring a Selenium course online or a tester seeking advanced test automation training, this guide covers both the "why" and the "how."
What is Selenium? A Quick Recap
Selenium is an open-source test automation tool for web applications. It supports multiple browsers, operating systems, and languages like Java, Python, and C#.
Key Selenium Components:
Selenium WebDriver – Automating browser actions
Selenium Grid – Runs tests in parallel across multiple machines
Selenium IDE – Record-and-playback tool for quick test creation
Selenium’s flexibility and community support make it the top choice in most test automation training curriculums.
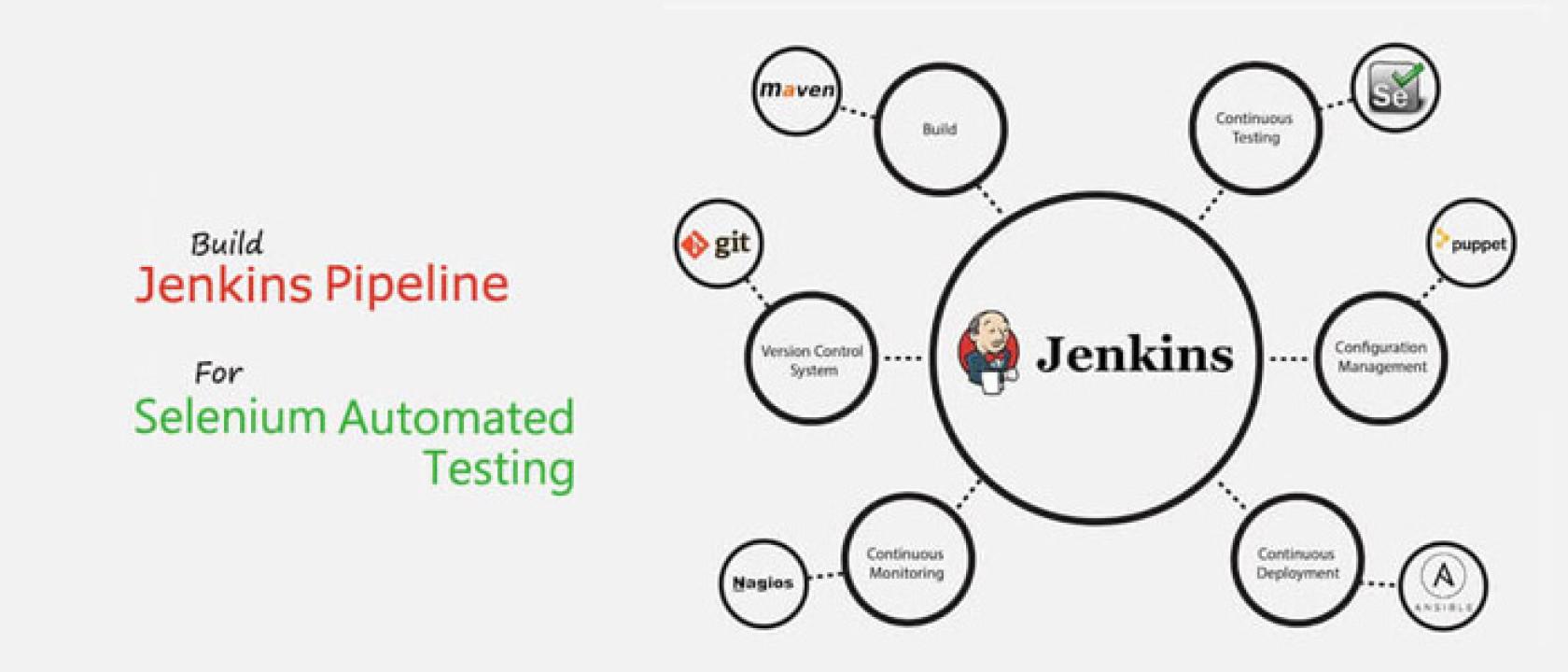
What is Jenkins? An Introduction to CI/CD
Jenkins is an open-source automation server used for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD). It automates various stages of software development including:
Code building
Testing
Deployment
You configure Jenkins using pipelines, either through GUI or a Jenkinsfile written in Groovy. Jenkins supports plugins for tools like Git, Docker, Maven, and, of course, Selenium.
Why Integrate Selenium with Jenkins?
1. Automated Testing in the Pipeline
Selenium tests can run automatically every time there’s a code change. This ensures:
Immediate bug detection
Reduced manual testing efforts
Higher confidence in deployment
2. Faster Feedback Loops
When Jenkins runs Selenium tests on each commit, developers receive instant feedback. This makes debugging faster and minimizes delays.
3. Parallel Test Execution
With Jenkins nodes and Selenium Grid, teams can run hundreds of tests in parallel, cutting test time drastically.
4. Improved Code Quality
Regular test automation identifies issues early, enforcing cleaner code standards.
Setting Up: Step-by-Step Selenium and Jenkins Integration
Let’s walk through how to configure Jenkins to run Selenium WebDriver tests using a Maven project as an example. This process is an essential part of test automation training, as it provides hands-on experience with integrating Jenkins and Selenium. The steps outlined here will give you a clear understanding of how to automate tests within a CI/CD pipeline, an essential skill for any test automation professional.
By following these instructions, you'll not only be able to set up Jenkins for Selenium WebDriver but also gain practical experience in streamlining the testing process as part of your test automation journey.
Step 1: Install Jenkins
Download Jenkins from https://www.jenkins.io
Run the installer and set up a default admin user.
Install necessary plugins: Maven Integration, GitHub, Selenium, and JUnit.
Step 2: Create a Maven Selenium Project
Create a new Maven project with the following structure:
swift
project-root/
├── pom.xml
└── src/test/java/com/example/tests/
└── LoginTest.java
Sample pom.xml Snippet:
xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>4.14.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Step 3: Write a Selenium Test Script
java
public class LoginTest {
WebDriver driver;
@Before
public void setUp() {
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
driver = new ChromeDriver();
}
@Test
public void loginPageTest() {
driver.get("https://example.com/login");
driver.findElement(By.id("username")).sendKeys("admin");
driver.findElement(By.id("password")).sendKeys("password");
driver.findElement(By.id("login")).click();
assertEquals("Dashboard", driver.getTitle());
}
@After
public void tearDown() {
driver.quit();
}
}
Step 4: Configure Jenkins Job
Go to Jenkins dashboard → New Item → “Maven Project”
Set the Git repository URL
Configure build triggers:
Example: “Poll SCM” or “Build after every push”
In Build section:
Set Goals to: clean test
Step 5: View Test Reports
Add the JUnit Plugin to Jenkins. Under "Post-build Actions", select Publish JUnit test result report, and set the path to:
bash
CopyEdit
target/surefire-reports/*.xml
Jenkins will now show pass/fail charts for Selenium test runs.
Advanced CI/CD Features with Selenium and Jenkins
1. Parallel Test Execution with Selenium Grid
Use Selenium Grid to distribute tests across multiple nodes. Configure Jenkins to trigger tests on different machines or containers.
2. Docker-Based Selenium Testing
Run Selenium in Docker containers to avoid local environment issues.
Use Docker Compose to spin up selenium/hub and selenium/node-chrome.
Jenkins pipeline can trigger tests inside these containers.
3. Headless Browser Testing
Run tests using Chrome or Firefox in headless mode to save resources:
java
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
options.addArguments("--headless");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(options);
4. Email Alerts and Slack Notifications
Use Jenkins plugins to notify teams of build status or test failures.
Real-World Use Case: Selenium + Jenkins at Scale
Case Study: An E-commerce Company
An e-commerce company with 30+ developers implemented Jenkins with Selenium. Before automation, their test cycle took 4 hours. After integrating:
Tests ran in 30 minutes using Selenium Grid
Bug detection rate improved by 60%
Developer feedback loop dropped from 2 days to 30 minutes
Selenium and Jenkins in DevOps Ecosystem
Jenkins Pipeline Code (Jenkinsfile) Example:
groovy
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
maven 'Maven 3.8.1'
}
stages {
stage('Checkout') {
steps {
git 'https://github.com/your/repo.git'
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh 'mvn clean compile'
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
sh 'mvn test'
}
}
stage('Report') {
steps {
junit 'target/surefire-reports/*.xml'
}
}
}
}
This pipeline runs Selenium tests after every code commit, automatically building and reporting results.
Benefits of Learning Selenium-Jenkins Integration
If you're exploring a Selenium course online or undergoing online Selenium training, mastering Jenkins integration gives you:
Real-world automation experience
DevOps readiness
Higher job opportunities
Strong portfolio projects
Recruiters actively look for professionals who can implement CI/CD in test automation. Completing a Selenium certification online with Jenkins projects increases your credibility.
Top Tools and Resources to Learn This Integration
To effectively learn how Selenium integrates with Jenkins for CI/CD, several top tools and resources can support your journey. Starting with courses, online Selenium training platforms like H2k Infosys offer hands-on tutorials that cover both Selenium automation and CI/CD workflows with Jenkins. These courses are structured to help learners gain practical skills in real-time testing environments.
For practice, leveraging GitHub along with Jenkins is highly recommended. Setting up repositories and integrating them into Jenkins pipelines allows you to simulate real-world testing scenarios, making your learning more applicable and job-ready.
If you're looking to validate your skills formally, pursuing a Selenium certification online is a smart move. Certifications demonstrate your expertise to employers and can significantly enhance your resume.
Lastly, the book "Continuous Testing for DevOps Professionals" is a valuable resource. It offers in-depth knowledge of CI/CD testing frameworks, best practices, and strategies, making it an excellent reference for anyone looking to deepen their understanding beyond tutorials.
Together, these resources provide a well-rounded foundation for mastering Selenium-Jenkins integration in a CI/CD pipeline.
Common Challenges & Solutions
When integrating Selenium with Jenkins, several challenges may arise, but each has a straightforward solution. One common issue is Jenkins not detecting Selenium tests; this can be resolved by ensuring that the test framework outputs results in XML format, which Jenkins uses to display test reports properly. Another challenge is when browser drivers fail in headless mode, often due to improper configurations. To fix this, you can use WebDriverManager to manage the drivers automatically and set the correct options for running the browsers in headless mode.
If Jenkins runs fail on the server, the issue might be related to the environment or missing configurations. To address this, it’s best to either set up Docker containers or properly configure Selenium Grid to distribute the load across multiple machines or nodes, ensuring consistent test execution. Lastly, if test execution is too slow, the solution is to parallelize the tests using Selenium Grid or leverage Jenkins agents for distributing the tests across multiple systems, significantly speeding up the execution process.
By understanding these common hurdles and applying the solutions, you can ensure a smoother integration between Selenium and Jenkins in your CI/CD pipeline.
Key Takeaways
Selenium automates web tests; Jenkins automates execution in CI/CD.
Integration allows automated testing on every code push.
Jenkins supports plugins and pipelines to manage Selenium runs.
Hands-on setup includes Maven projects, Git integration, and test reports.
Industry demands professionals skilled in test automation with CI/CD.
Conclusion
Selenium and Jenkins together power the backbone of modern automated testing. Mastering their integration is essential for today’s QA professionals.
Kickstart your journey today with online Selenium training and build your first CI/CD project.