Introduction
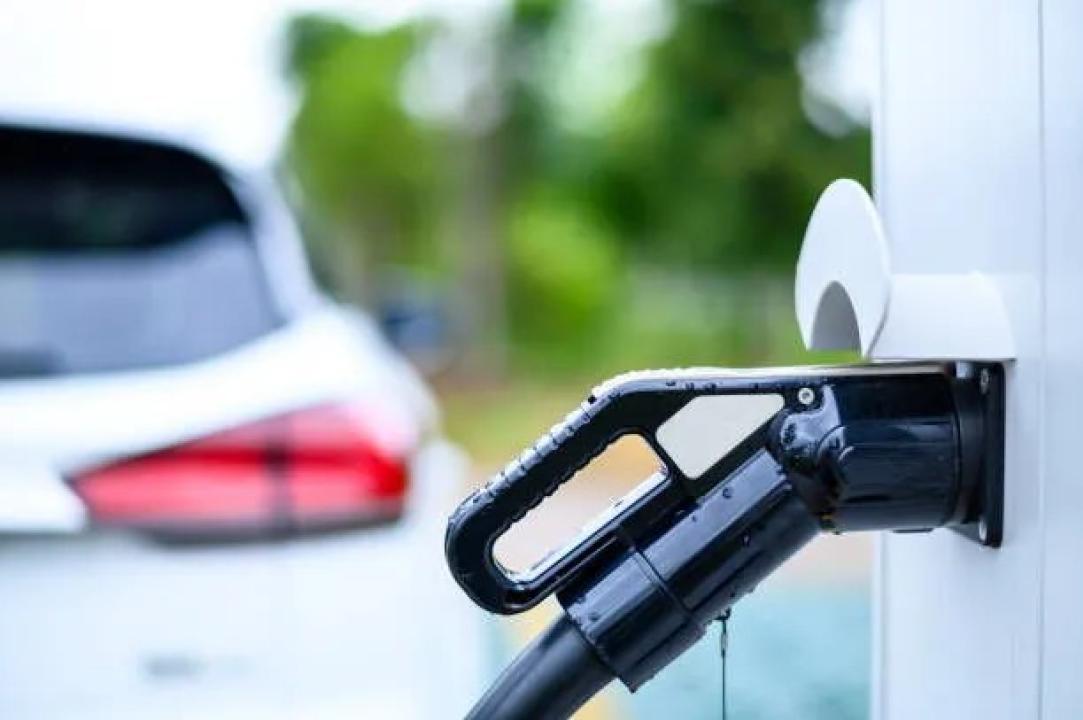
As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly popular, understanding the different types of charging connectors is essential for both current and potential China EV Charger owners. Charging connectors aren't universal; they vary based on the charging type (AC or DC), region, and vehicle manufacturer. This article explores the various EV charging connector types, their functionality, and their compatibility with different EVs. Whether you're charging at home, at work, or on the road, knowing the correct connector for your EV can ensure a smooth and efficient charging experience.
EV Charging Plug Types
AC Charging: The Everyday Charging Solution
AC (alternating current) charging is the most common form of EV charging and is ideal for daily use. AC charging is split into two levels: Level 1 and Level 2, catering to different needs, from slow overnight charging at home to quicker top-ups at public charging stations.
-
Level 1 Charging: The simplest and most convenient option, Level 1 charging uses a standard 120-volt household outlet and the cable that comes with your vehicle. While convenient, it charges slowly, adding around 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. It’s great for overnight charging or for drivers with short daily commutes. However, for faster charging, Level 2 is a better choice.
-
Level 2 Charging: Operating at 240 volts, Level 2 charging is much faster, providing up to 40 miles of range per hour. This requires a dedicated charging station, such as those found at homes, workplaces, shopping centers, and parking garages. For most EV owners, Level 2 is the go-to option due to its balance of speed and accessibility.
AC Connector Standards in North America
In North America, two key AC connector standards dominate:
-
SAE J1772: The universal standard for most non-Tesla EVs, supporting both Level 1 and Level 2 charging. These connectors are common at public charging stations.
-
NACS (Tesla Connector): Tesla's proprietary connector, primarily used by Tesla vehicles. However, Tesla’s recent efforts to open up its Supercharger network to other EVs could potentially expand the adoption of this standard.
DC Fast Charging: The Need for Speed
While AC charging is perfect for everyday use, DC fast charging is ideal for long trips or when you need a rapid charge. DC fast chargers bypass the vehicle's onboard charger and deliver power directly to the battery, significantly speeding up the charging process.
DC Fast Charging Connectors in North America
In North America, there are three primary DC fast charging connectors: SAE Combo (CCS1), CHAdeMO, and NACS. Each has unique features and compatibility:
-
SAE Combo (CCS1): The Combined Charging System (CCS) is a versatile connector that supports both AC and DC charging. CCS1, used in North America, is based on the SAE J1772 connector but includes two additional DC pins, enabling fast charging. It supports power levels up to 350 kW, making it one of the fastest charging options available.
-
CHAdeMO: Developed in Japan, CHAdeMO was one of the earliest DC fast charging standards but is being overshadowed by CCS. However, it remains in use, especially for older EVs from Japanese manufacturers.
-
NACS (Tesla Connector): Tesla's NACS connector supports both AC and DC fast charging. Though used mainly by Tesla vehicles, Tesla’s push to open its Supercharger network to other EVs might lead to greater adoption of this standard.
The Rise of High-Power DC Chargers
As EV technology advances, the need for faster charging solutions has led to the development of high-power DC chargers. While 50 kW chargers remain common, higher power options like 150 kW, 270 kW, and even 350 kW chargers are becoming increasingly available. These powerful chargers can add hundreds of miles of range in just minutes, making them ideal for long-distance travel.
CCS: The Global Standard for DC Fast Charging
CCS has become the leading DC fast charging standard worldwide. It offers a streamlined design and robust power capabilities, making it a favorite among automakers and charging network operators.
-
CCS Type 1 and Type 2:
-
CCS Type 1: Used mainly in North America, based on the SAE J1772 connector, with two additional DC pins.
-
CCS Type 2: Used in Europe, based on the Mennekes Type 2 connector, and also featuring two extra DC pins.
-
Advantages of CCS
One of the biggest benefits of CCS is that it supports both AC and DC charging through a single connector. This simplifies the vehicle design and eliminates the need for multiple charging ports. Additionally, CCS supports high-power levels (up to 350 kW), which makes it suitable for the latest fast-charging solutions.
Challenges and Compatibility
Despite its benefits, CCS connectors are not compatible with CHAdeMO or GB/T charging stations, which use different communication protocols. While adapters exist, they can be hard to find and may not always offer the best charging experience.
CHAdeMO: A Niche but Important Standard
CHAdeMO remains a significant charging standard, particularly for older EVs from Japanese manufacturers. Although its popularity has waned due to the rise of CCS, it still plays an important role in the EV landscape.
Key Features of CHAdeMO
-
Bidirectional Charging: One of the standout features of CHAdeMO is its support for bidirectional charging, allowing vehicles to send power back to the grid or a home—useful for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications.
-
Compatibility: CHAdeMO connectors are not compatible with CCS or GB/T stations, which limits their use in regions where these standards dominate.
The Future of CHAdeMO
While CCS continues to rise in popularity, CHAdeMO's bidirectional capabilities may ensure its continued relevance in niche applications.
GB/T: The Chinese Standard
In China, the GB/T standard is the primary connector for both AC and DC charging, with most Chinese-made EVs using this connector.
Key Features of GB/T
-
AC and DC Charging: Like CCS, GB/T connectors support both AC and DC charging.
-
High-Power Capabilities: GB/T connectors can handle power levels up to 250 kW, enabling fast charging.
Global Impact of GB/T
Though primarily used in China, the influence of GB/T is expanding as Chinese automakers grow internationally. However, its incompatibility with CCS and CHAdeMO could hinder its adoption outside China.
NACS: Tesla’s Proprietary Connector
Tesla’s NACS connector is unique, supporting both AC and DC fast charging. Currently used mainly by Tesla vehicles, Tesla’s move to open its Supercharger network could lead to wider adoption of this connector.
Advantages of NACS
-
Compact Design: NACS is smaller and more compact than CCS or CHAdeMO, making it easier to handle and install.
-
High-Power Capabilities: NACS supports power levels up to 250 kW, suitable for rapid charging.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its advantages, NACS is limited to Tesla vehicles for now. The company’s efforts to open the Supercharger network to other automakers could increase adoption, but its proprietary nature and lack of compatibility with other standards may limit its appeal.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Connector for Your EV
As the EV market evolves, understanding the different charging connector types is crucial for maximizing the charging experience. Whether you’re charging daily with AC or using DC fast charging for longer trips, selecting the correct connector will make your experience smoother. As charging solutions become more standardized and high-power chargers become more common, the future of EV charging looks promising. By staying informed, you can ensure that you’re using the best charging solution for your EV.Know more about Google SEO Directory