In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, resource recovery and value creation from end-of-life (EOL) products have emerged as powerful tools for sustainability and profitability. As businesses and governments face mounting pressure to reduce waste and improve environmental performance, innovative recycling and resource recovery strategies offer a pathway not just to compliance—but to new revenue streams. At the core of this transition lies the circular economy model, which aims to minimize waste, maximize resource efficiency, and transform EOL products into valuable raw materials or reusable components.
End-of-life products, ranging from electronic devices and vehicles to packaging materials and industrial machinery, often contain valuable metals, plastics, and other recoverable substances. Traditionally, these items were discarded in landfills or incinerated, contributing to pollution and resource depletion. However, with advancements in material recovery technologies and a growing market for recycled inputs, companies now have the opportunity to recapture value from what was once considered waste. This shift not only reduces environmental impact but also creates new business models focused on remanufacturing, refurbishment, and secondary materials trading.
The economic potential is substantial. For instance, recycling rare earth elements from discarded electronics or extracting precious metals from circuit boards can be far more cost-effective than sourcing virgin materials. Similarly, reusing plastics and metals in the manufacturing sector reduces dependency on raw material imports and lowers production costs. These practices support the development of domestic supply chains, reduce carbon emissions, and enhance long-term economic resilience. Moreover, regulatory frameworks such as Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) are encouraging manufacturers to take accountability for the entire lifecycle of their products, thereby promoting investment in collection and recycling infrastructure.
Beyond environmental and economic benefits, resource recovery plays a key role in job creation and skill development. Recycling, dismantling, and refurbishment industries require a skilled workforce to operate sorting machines, manage logistics, and perform technical tasks. As the green economy expands, so does the demand for trained professionals in waste management and circular business models. This creates opportunities not only for entrepreneurs but also for workers in both formal and informal sectors.
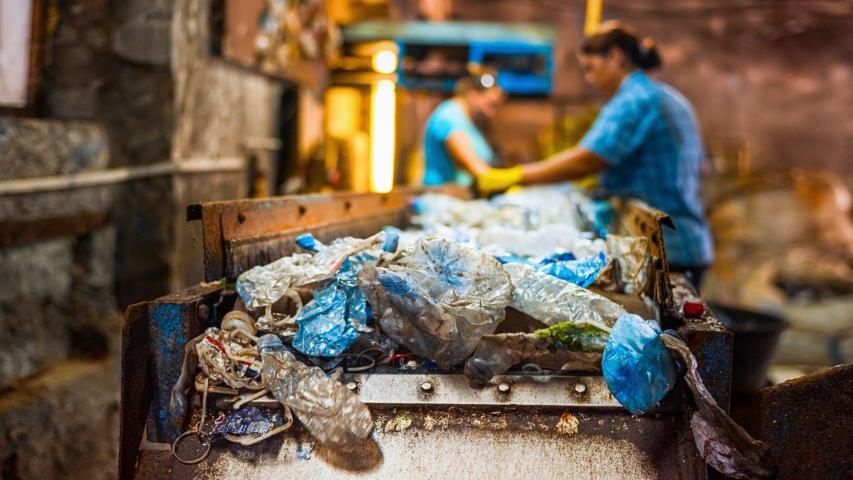
One of the most pressing areas of concern—and opportunity—is e-waste. With the exponential growth of consumer electronics, India is witnessing a significant increase in discarded gadgets and appliances. This e-waste contains valuable metals like gold, silver, copper, and palladium, which can be extracted and reused. Setting up formalized e-waste recycling and dismantling plants is essential for managing this waste efficiently and safely.
Agile Regulatory’s E-Waste Recycling & Dismantling Plant Setup Services
Agile Regulatory assists businesses and entrepreneurs in setting up authorized e-waste recycling and dismantling plants across India. From obtaining necessary consents from State Pollution Control Boards to guiding through CPCB authorization, we offer end-to-end support to ensure legal compliance and efficient operational setup. Our expert team helps in designing plant layout, machinery selection, and documentation—enabling clients to tap into the growing e-waste market. With increasing focus on circular economy and mandatory EPR compliance, establishing a recycling facility is not just an environmental responsibility but a profitable business opportunity. Agile Regulatory simplifies the process and empowers enterprises to become leaders in green innovation.
By embracing resource recovery and creating value from end-of-life products, businesses can future-proof their operations, reduce environmental footprints, and unlock new income streams. As the world shifts towards sustainability, early movers in this space will be best positioned to lead the transition to a circular, resilient, and economically robust future.