In industries where sterilization is critical, such as healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, the importance of reliable sterilization processes cannot be overstated. One essential technique to guarantee the effectiveness of sterilization cycles is Autoclave Temperature Mapping. This process helps ensure that autoclaves operate within precise temperature ranges, providing confidence that all equipment and materials are properly sterilized.
What is Autoclave Temperature Mapping?
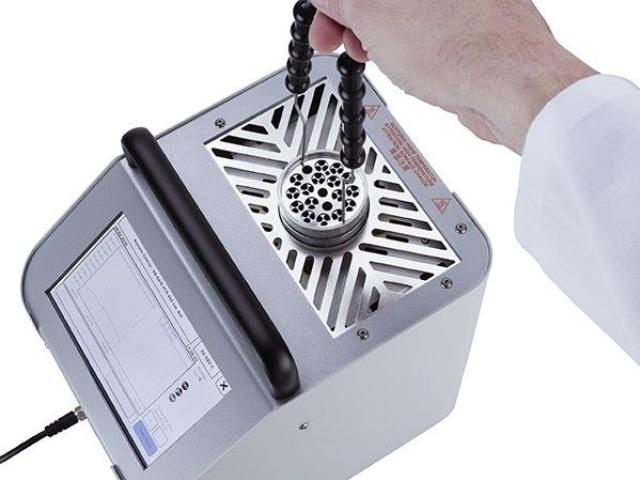
Autoclave Temperature Mapping is a systematic process that measures and records temperature variations within an autoclave chamber during a sterilization cycle. The goal is to identify temperature distribution and detect any cold or hot spots that might compromise sterilization.
An autoclave sterilizes by using pressurized steam at specific temperatures and durations. However, due to variations in chamber size, loading patterns, and equipment design, temperatures can vary across different areas inside the autoclave. Temperature mapping helps identify these discrepancies by placing multiple sensors throughout the chamber to log temperature readings in real-time.
Why is Autoclave Temperature Mapping Important?
Sterilization must meet strict regulatory standards to ensure the elimination of harmful microorganisms. If the temperature within any part of the autoclave chamber falls below the required sterilization temperature, it can result in incomplete sterilization, posing serious safety risks.
Autoclave Temperature Mapping allows users to:
- Verify that the autoclave achieves the required temperature throughout the entire chamber.
- Identify zones with inconsistent heating that could compromise sterilization.
- Optimize loading procedures to improve steam penetration and temperature uniformity.
- Comply with industry standards and regulatory requirements such as FDA, ISO, and GMP guidelines.
By regularly conducting temperature mapping, facilities can maintain consistent sterilization quality and reduce the risk of product contamination or recalls.
How is Autoclave Temperature Mapping Conducted?
The process typically involves the following steps:
1. Planning the Mapping Study
Before starting, a detailed plan is made to determine sensor placement and sterilization cycle parameters. Sensors are placed in critical locations including corners, door areas, and spots furthest from steam injection points.
2. Installing Sensors
Specialized temperature probes or data loggers capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures are installed at designated locations within the autoclave chamber. These devices continuously record temperature data throughout the cycle.
3. Running the Sterilization Cycle
The autoclave runs a standard sterilization cycle as per operational protocols while the sensors capture temperature data.
4. Data Analysis
After the cycle, the recorded temperature data is downloaded and analyzed. Graphs and temperature profiles highlight any variations or deviations from the required sterilization temperature.
5. Reporting and Action
A comprehensive report is generated, documenting whether the autoclave met the sterilization criteria. If temperature inconsistencies are found, corrective actions such as equipment maintenance, adjustment of cycle parameters, or changes in loading patterns are recommended.
Benefits of Autoclave Temperature Mapping
Ensures Sterilization Effectiveness
By confirming uniform temperature distribution, temperature mapping guarantees that every part of the load reaches the necessary sterilization temperature, ensuring patient safety and product integrity.
Improves Process Validation
Mapping data provides documented evidence required for validation and regulatory audits, demonstrating compliance with sterilization standards.
Enhances Equipment Performance
Identifying hotspots or cold zones allows preventive maintenance and calibration of the autoclave, extending equipment lifespan and reliability.
Optimizes Load Configuration
Understanding temperature variations helps optimize how instruments or materials are placed within the chamber to improve steam circulation and sterilization efficiency.
Industries That Rely on Autoclave Temperature Mapping
- Pharmaceuticals: Sterilization of drug manufacturing equipment and components requires strict adherence to temperature standards, making temperature mapping essential for regulatory compliance.
- Food Processing: Autoclaves used for food sterilization and canning rely on temperature mapping to guarantee food safety and extend shelf life.
- Biotechnology: Laboratories use autoclaves for sterilizing biological materials, and temperature mapping ensures precise control over sterilization parameters.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics use autoclaves to sterilize surgical instruments, lab equipment, and medical waste. Temperature mapping helps ensure patient safety by validating sterilization processes.
Choosing the Right Autoclave Temperature Mapping Solution
Selecting an appropriate temperature mapping system involves considering several factors:
- Sensor Quality: Probes must accurately record high temperatures and resist steam and pressure effects.
- Data Logging Capacity: Devices should support continuous recording and have sufficient memory for complete cycle data.
- Software Features: User-friendly software for data visualization, analysis, and reporting is crucial for efficient interpretation.
- Compliance: The system should meet industry standards for validation and documentation.
Conclusion
Autoclave Temperature Mapping is a vital process that ensures sterilization cycles are effective, reliable, and compliant with strict safety regulations. By providing detailed temperature data from multiple points within the autoclave chamber, it helps identify inconsistencies that could compromise sterilization outcomes.
Regular temperature mapping not only safeguards patient health and product quality but also supports regulatory compliance and operational efficiency. Whether in healthcare, pharmaceuticals, or food processing, investing in robust autoclave temperature mapping solutions is a critical step toward achieving consistent and validated sterilization processes.