Which Camera Settings Matter Most for Street Photography?
Street photography is one of the most authentic and unpredictable genres of photography. It captures real-life moments—unposed, raw, and full of emotion. But to make those fleeting seconds stand out, understanding your camera settings is crucial. Whether you’re using a compact mirrorless camera or a professional DSLR, the right balance of exposure, shutter speed, and focus can turn an ordinary scene into a storytelling masterpiece.
In this guide, we’ll break down which camera settings matter most for street photography and how to fine-tune them for different lighting and motion conditions.
The Importance of Settings in Street Photography
Street photography demands spontaneity. You don’t have time to adjust every setting for each shot. That’s why knowing your camera well and setting it up for fast reaction is essential. The best street photographers don’t rely solely on equipment—they rely on intuition, supported by camera settings that allow them to respond instantly to what’s unfolding around them.
A great shot often comes down to three fundamental exposure settings: shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. Each plays a unique role in shaping the look and feel of your photos.
1. Shutter Speed – Freezing or Embracing Motion
Shutter speed determines how motion is captured in your photo. A fast shutter freezes time, while a slower one allows movement blur to create dynamic energy.
For street photography, you’ll typically want to use a shutter speed between 1/250s and 1/500s to freeze human movement while walking. However, if you want to add motion blur—like cars rushing past a still pedestrian—experiment with slower speeds such as 1/60s or 1/125s.
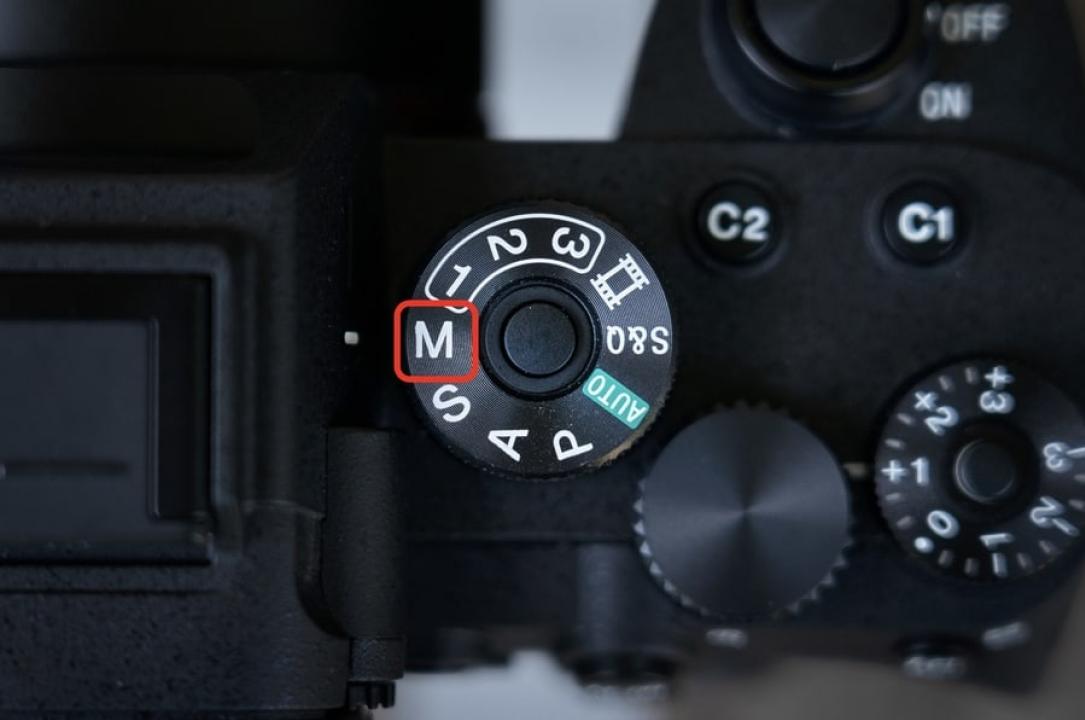
Using Shutter Priority Mode (S or Tv) is a smart choice for beginners. It allows the camera to automatically adjust aperture while you focus on controlling motion.
2. Aperture – Controlling Depth and Focus
Aperture affects how much of your scene is in focus. A wide aperture (like f/1.4 or f/2.8) creates beautiful background blur, isolating your subject from the environment. A narrower aperture (f/8 or higher) keeps more elements sharp, ideal for busy urban scenes.
Street photographers often prefer settings around f/5.6 to f/8, as this gives enough depth of field to capture subjects in motion without losing sharpness. Compact primes from brands like Sigma are especially popular for this purpose, offering bright apertures and stunning sharpness in small, lightweight lenses—perfect for photographers who prefer shooting discreetly in crowded streets.
3. ISO – Adapting to Light Changes
Street lighting conditions can change instantly—from bright sunlight to dim alleys or shadowed buildings. ISO controls your camera’s sensitivity to light.
For daylight shooting, keep your ISO low (around 100–400) to retain detail and reduce noise. As evening approaches, you may need to raise it to 800–1600 or higher depending on your camera’s performance. Modern sensors handle higher ISOs much better, so don’t hesitate to increase it if the moment demands it.
Many street photographers use Auto ISO with a maximum cap set around 1600 or 3200. This allows you to maintain a consistent shutter speed and aperture while the camera adjusts sensitivity on the fly.
4. Focus Mode – Staying Ready for Action
Autofocus speed and accuracy are critical for street photography. People move unpredictably, and a missed focus can ruin an otherwise perfect composition.
Most professionals rely on Continuous Autofocus (AF-C) mode, which tracks moving subjects. Pair this with Zone or Wide-Area AF to cover a broader portion of the frame. If you’re shooting static scenes, Single AF (AF-S) works well for precise focusing.
For ultimate control, many seasoned photographers pre-focus manually. This technique, known as zone focusing, involves setting your focus distance manually (usually around 2–3 meters) and shooting quickly when subjects enter that zone.
5. White Balance – Maintaining Natural Tones
Urban environments often feature mixed lighting—streetlights, neon signs, and sunlight bouncing off glass surfaces. Setting your White Balance (WB) correctly ensures that your images reflect accurate colors.
While Auto White Balance performs well in most cases, switching to presets like Daylight, Cloudy, or Tungsten can help maintain consistency. For night shooting, slightly warmer tones can make your photos feel more atmospheric.
6. Shooting Mode – RAW vs JPEG
Shooting in RAW format gives you maximum flexibility when editing, especially when correcting exposure or color later. RAW files capture more dynamic range, making them ideal for street photography where lighting varies drastically.
If you need faster workflow or smaller file sizes, JPEG works well—but remember, it limits post-processing flexibility. Many professionals prefer shooting RAW+JPEG to have both options ready.
7. Metering Mode – Getting the Exposure Right
Metering tells your camera how to evaluate light in a scene. For unpredictable environments, Evaluative or Matrix Metering usually works best—it considers the entire frame to balance exposure.
If your subject is backlit or under harsh lighting, Spot Metering allows you to expose correctly for their face or specific details.
Additional Settings to Consider
-
Burst Mode: Ideal for capturing fleeting moments—press and hold the shutter to shoot a quick series of frames.
-
Silent Shutter: Helps you shoot unnoticed in quiet environments, preserving candid expressions.
-
Custom Buttons: Assign focus lock or ISO adjustment to easy-access buttons to react faster.
Recommended Gear for Street Photographers
Street photographers favor compact, lightweight cameras with quick autofocus and great low-light capability. Mirrorless cameras from Sony, Fujifilm, and Canon are popular choices, often paired with small prime lenses.
High-quality yet portable lenses like SIGMA’s 35mm or 56mm f/1.4 offer excellent sharpness and bokeh without drawing unwanted attention. For photographers in Pakistan looking for genuine and reliable gear, the nisbat road camera market is a well-known destination where professionals and enthusiasts explore a wide range of camera accessories and lenses.
Tips for Better Street Photography
-
Anticipate the Moment: Keep your camera on and ready. Great shots often appear suddenly.
-
Blend In: Use smaller cameras or neutral colors to stay unnoticed.
-
Work with Light: Use shadows, reflections, and contrast to add drama to your compositions.
-
Tell a Story: Focus on emotion, interaction, and human presence rather than technical perfection.
-
Practice Patience: Street photography rewards those who observe rather than chase.
Conclusion
Mastering camera settings for street photography is about balancing control with intuition. The best results come when technical understanding meets creative timing. Shutter speed freezes or enhances motion, aperture defines your depth, ISO adapts to changing light, and focus ensures sharp results. When used together effectively, these settings help you tell real, powerful stories through your lens.
Compact prime lenses from trusted brands like Sigma further elevate your results, providing the clarity and speed that street environments demand. Whether you’re exploring local markets, city streets, or urban nightlife, the right combination of gear and settings can transform ordinary moments into unforgettable images.