Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has become a game-changer for enterprises looking to enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and streamline repetitive tasks. By integrating software robots into everyday business processes, organizations can achieve faster results while freeing human employees to focus on strategic initiatives. Understanding the most effective RPA Software Use Cases is essential for companies aiming to maximize their automation investments.
Benefits of RPA in Enterprises
Implementing RPA in enterprise workflows offers multiple benefits, including:
Increased Efficiency: Automated processes operate 24/7 without delays or breaks.
Cost Reduction: Fewer manual errors and reduced labor costs lower operational expenses.
Enhanced Accuracy: RPA robots follow predefined rules, ensuring error-free execution.
Scalability: Enterprises can scale automation efforts based on demand.
Better Compliance: Automated workflows maintain consistent audit trails, aiding regulatory compliance.
These advantages make RPA a valuable tool across industries, particularly for large enterprises managing complex operations.
Key RPA Software Use Cases
Enterprise adoption of RPA spans various departments and processes. Here are some of the most impactful RPA Software Use Cases:
1. Finance Automation
Finance departments benefit significantly from RPA. Robots can handle tasks such as invoice processing, accounts reconciliation, and financial reporting. By automating these repetitive functions, companies reduce errors and improve cycle times, enabling finance teams to focus on strategic planning.
2. HR Onboarding
Human Resources can leverage RPA to streamline employee onboarding. Automated workflows can manage background checks, document verification, and system access setup. This ensures new hires are onboarded quickly and accurately, improving overall employee experience.
3. Customer Support
Customer service teams often deal with high volumes of repetitive queries. RPA bots can manage ticket routing, respond to FAQs, and update customer records automatically. These RPA Use Cases enhance response times and allow human agents to handle more complex interactions.
4. Data Processing
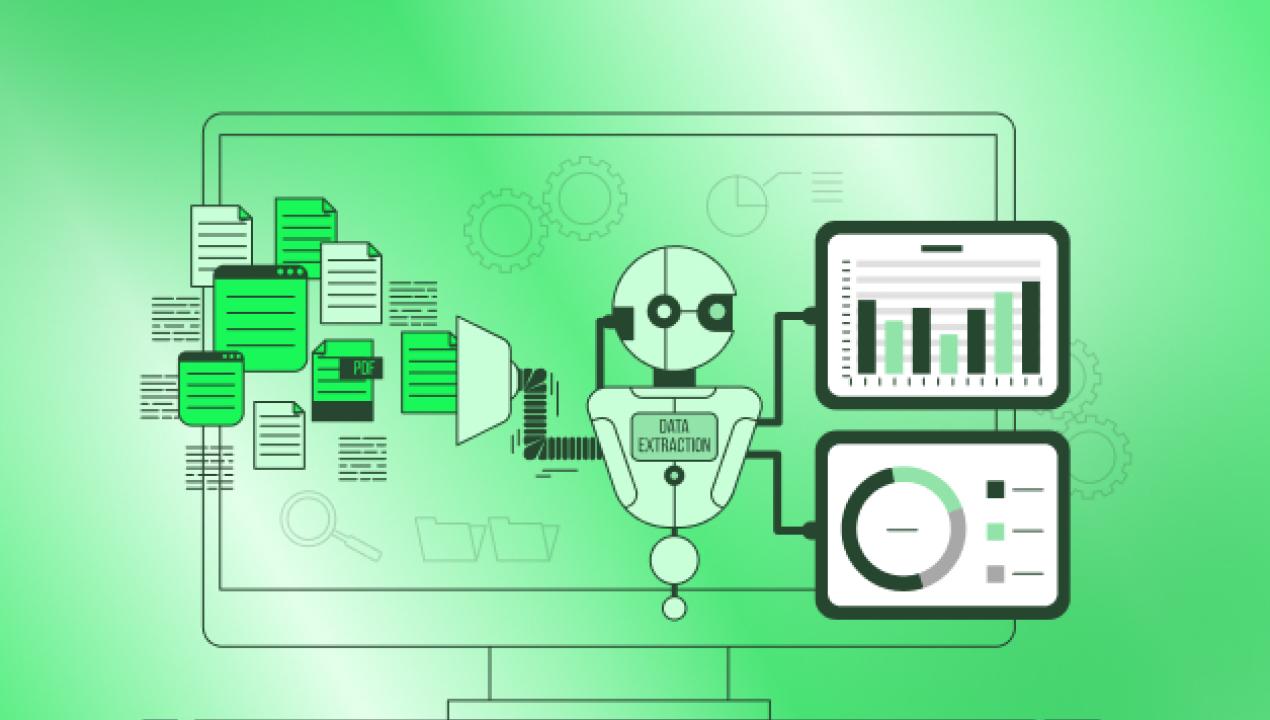
Data-intensive tasks like data extraction, validation, and migration can be automated using RPA. Enterprises often rely on software robots to handle large datasets efficiently, minimizing errors while speeding up decision-making processes.
5. IT Operations
IT teams use RPA to automate routine maintenance, system monitoring, and user account management. Automated workflows reduce downtime, ensure compliance with security policies, and free IT staff to focus on higher-value initiatives.
Future of RPA in Enterprise Workflows
The future of RPA looks promising, with advanced technologies like AI and machine learning enhancing automation capabilities. Intelligent RPA can now handle unstructured data, make predictive decisions, and optimize processes dynamically. Enterprises investing in RPA Development Services can build scalable, adaptable automation strategies to stay competitive in a digital-first landscape.
Conclusion
RPA is no longer a futuristic concept—it is a practical solution transforming enterprise workflows. From finance and HR to IT and customer service, these RPA Software Use Cases illustrate the potential of automation to drive efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Companies that adopt RPA strategically can unlock significant operational benefits and prepare for the next wave of intelligent automation.