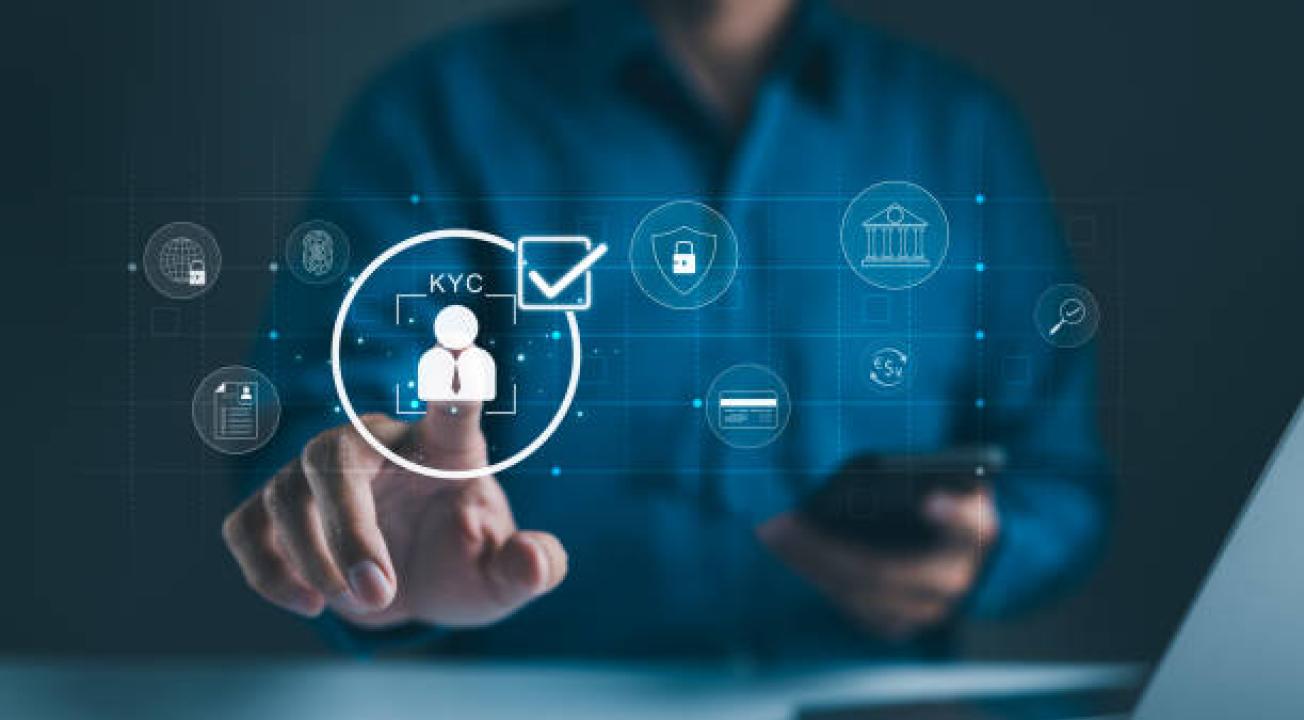
Financial crime, identity theft, and fraud are more advanced than ever in the digital economy. Banks, fintech companies and international companies are under pressure to protect the data of their customers and adhere to the regulations. The core of these activities is KYC verification, which is an important procedure that helps to verify that the customers are who they say they are.
However, what is KYC verification, and why is it regarded as a pillar of the contemporary compliance models? This paper discusses the purpose, process and future of KYC and in-depth KYC compliance, KYC checks, KYC verification online and the effects of KYC regulations.
What is KYC Verification?
KYC verification, also known as Know Your Customer verification, is the procedure of establishing and authenticating the identity of a customer prior to them using financial services. The aim is to avert unlawful practices like money laundering, terrorist funding, and fraud.
It is not only a process of checking names and documents but also of knowing the risk profile of the customers and tracking their activities as time goes by.
Key aspects of KYC verification include:
Customer Identity Checks – Confirming identity with official documents.
Address Verification- Securing a verifiable and valid residence.
Risk Assessment - The assessment of financial or reputational risk of a customer.
Constant Surveillance- The constant review of transactions to identify suspicious activity.
The Evolution of KYC Verification
KYC requirements are not new but became more popular in the early 2000s when the world started to fight the problem of money laundering. In the first place, the process of verification was mostly manual, as it included the collection of documents physically and their checking in person.
KYC verification online has transformed the process today. Companies can perform identity verification in a few seconds with the help of AI, biometrics, and real-time databases. This digital transformation does not only improve customer experience but also improves compliance.
The Core Principles of KYC Compliance
KYC compliance is not a mere regulatory box, but a business, customer and financial ecosystem protection framework. Any organization that does not adhere to the KYC standards is exposed to hefty fines, damaged reputation, and prosecution.
The key principles of KYC compliance include:
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) - Gathering the correct personal information of customers.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) - Using more rigorous checks on high-risk individuals/entities.
Continuous Surveillance - Tracking of customer transactions to detect anomalies.
Record-Keeping- Keeps a detailed record of KYC checks to be audited and to regulators.
KYC Checks: How They Work
KYC checks are the foundation of the verification procedure. Such checks are used to verify that the person requesting access to services is valid.
1. Document Verification
IDs such as passports, driver licenses or national identity cards are provided by customers. High-tech systems confirm the authenticity of such documents with the official databases.
2. Biometric Verification
The KYC solutions of today usually involve facial recognition and fingerprint scanning to compare physical characteristics with the documents provided.
3. Address Verification
They require evidence of residence in the form of utility bills or bank statements to verify the place of residence of the individual.
4. Sanctions & Watchlist Screening
KYC checks involve screening the customers against global watchlists, sanctions databases, and politically exposed persons (PEP) lists.
5. Continuous Monitoring
KYC does not end with onboarding. Unusual activity is monitored on transactions to maintain continued compliance.
The Role of KYC Verification Online
KYC online verification has become the trend with the emergence of digital banking, cryptocurrency exchanges, and international e-commerce. Customers can now do verification remotely instead of visiting the premises.
Benefits of online KYC include:
Speed- Checking can be done within minutes as opposed to days.
Accessibility- Remote customers do not have to travel to access financial services.
Precision -Automated systems minimize human error in document validation.
Scalability - Thousands of KYC checks can be made at a time by the business.
There is also AI-based fraud detection in online verification, which means that fake documents or stolen identities are identified as soon as possible.
Global KYC Regulations and Standards
KYC rules are influenced by the international organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), and national laws of the respective countries. These laws form the guidelines that businesses should adhere to in order to be compliant.
Among the major regulations, there are:
FATF Recommendations – Global standards for AML and CTF.
EU AML Directives – Strict KYC compliance requirements for financial institutions across Europe.
USA PATRIOT Act – Mandates KYC checks for all U.S. financial institutions.
Asia-Pacific AML Laws -Countries such as Singapore and Japan have strong KYC verification systems.
Although the requirements are different depending on the region, the aim is the same: to prevent financial crimes and ensure the financial stability of the world.
Industries that require KYC Checking
KYC verification has been extended to other sectors, although traditionally the banking sector is linked with it:
Fintech & Digital Banks - To onboard customers safely and in line with AML laws.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges - To fight illegal trading and to satisfy international standards.
E-commerce & Market places- To avoid fraud and safeguard buyers and sellers.
Insurance & Healthcare- To authenticate the policyholders and minimize fraudulent claims.
Real Estate - To verify the legitimacy of buyers and sellers and to avert money laundering.
Challenges in KYC Verification
Although it is a necessary requirement, KYC has its challenges:
Data Privacy Issues- Customers are concerned about the way their personal information is kept.
False Positives- Automated systems can mis-flag valid users.
International Differences - Various jurisdictions have dissimilar KYC regulations, which makes it difficult to comply.
Friction to customers- Prolonged KYC procedures may irritate the customers and cause drop-offs.
The solution to these challenges lies in the balancing of strong compliance and easy user experiences.
The Future of KYC Verification
In the future, online KYC verification will be further developed. The new technologies, such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and digital IDs, will transform verification.
Blockchain for Identity Management
Secure access and reduction of fraud can be achieved by immutable digital identities stored on blockchain.
AI & Machine Learning
KYC checks are powered by AI and can process large amounts of data in real time, identifying anomalies that human reviewers might overlook.
Global Digital Identity Systems
Universal identity frameworks can enable smooth cross-border KYC validation.
Biometric Expansion
Remote onboarding will become the norm of facial recognition, iris scanning, and voice recognition.
Conclusion: Why KYC Verification is the Pillar of Trust
KYC verification is no longer a choice in the age of blistering digital change, but a requirement. Since knowing what KYC verification is to conduct effective KYC checks and adhering to KYC regulations, businesses should focus on identity verification to succeed in a secure and compliant manner.
The process will keep on evolving as more industries adopt KYC verification online, making it faster, smarter and customer friendly. Finally, trust is built on strong KYC compliance that helps to conduct safer transactions, protect businesses, and enhance the global financial system.