Introduction
Types of Ceiling Occupancy Sensors
Ceiling occupancy sensors come in various types, each catering to specific needs and scenarios. Here, we explore the most common sensor technologies that have revolutionized the way spaces are managed.
Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensors
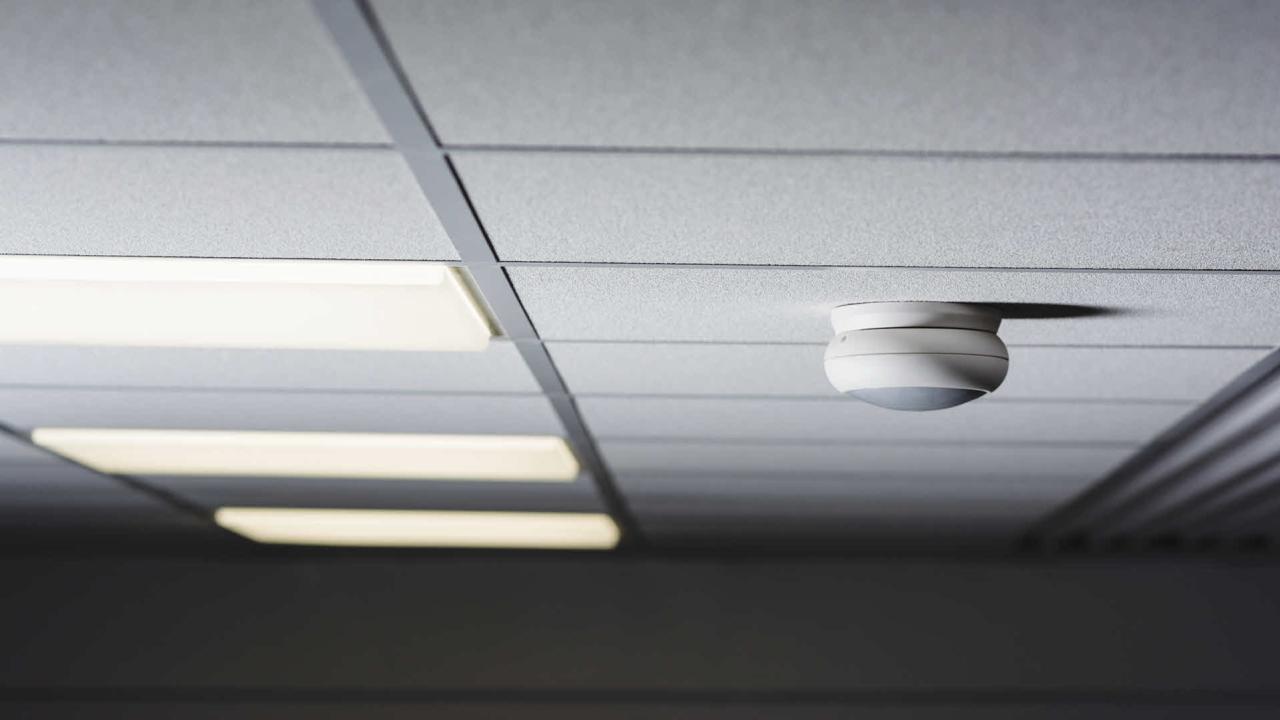
Description: PIR sensors are one of the most popular types of ceiling occupancy sensors. They operate based on detecting infrared radiation emitted by the human body.
Features and Working Principle: PIR sensors consist of pyroelectric materials that generate an electric charge when exposed to infrared radiation. These sensors have two pyroelectric sensors with a lens to focus on the detection area. When a person moves within the sensor’s field of view, the change in infrared radiation activates the sensor, triggering the control of lighting or other devices.
Applications: PIR sensors find widespread use in office spaces, conference rooms, hallways, and restrooms, providing energy-efficient lighting control.
Ultrasonic Sensors
Description: Ultrasonic ceiling occupancy sensors rely on sound waves to detect movement.
Features and Working Principle: These sensors emit ultrasonic waves and measure the time taken for the waves to bounce back after hitting an object or person. If there is any movement within the detection range, the time delay changes, signaling the presence of an occupant.
Applications: Ultrasonic sensors are ideal for spaces with obstructions or where direct line-of-sight detection is challenging, such as storage rooms and restrooms.
Dual-Technology Sensors
Description: Dual-technology sensors combine PIR and ultrasonic technologies for enhanced accuracy and reliability.
Features and Working Principle: These sensors require both PIR and ultrasonic signals to be triggered. The dual verification minimizes false activations and ensures precise occupancy detection.
Applications: Dual-technology sensors are suitable for areas where accurate and reliable detection is crucial, such as classrooms and healthcare facilities.
Microwave Sensors
Description: Microwave sensors use microwave signals to sense motion.
Features and Working Principle: These sensors emit continuous microwave signals and measure the frequency shift caused by movement within the monitored area. They offer wide coverage but might be affected by physical barriers.
Applications: Microwave sensors are preferred for high-security areas, parking lots, and open spaces.