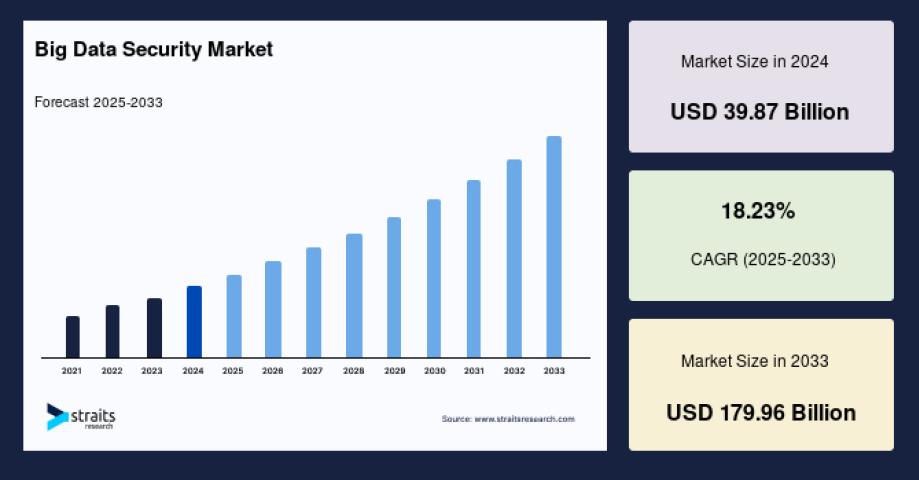
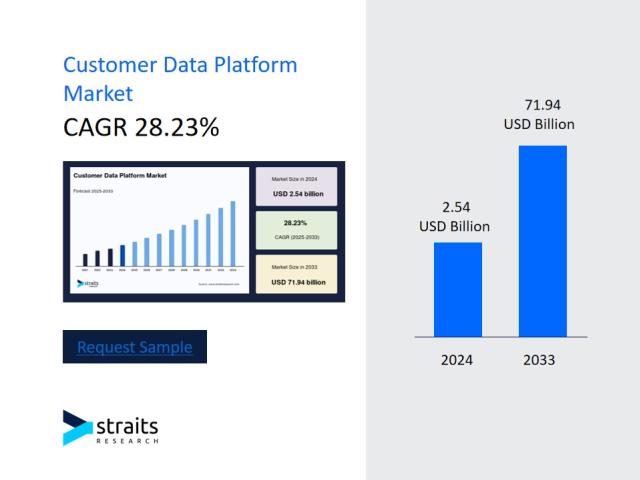
In today’s digital economy, businesses rely heavily on data to make strategic decisions, improve customer experiences, and enhance operational efficiency. This has created a growing demand for professionals skilled in managing and transforming complex data systems. Data engineer jobs play a crucial role in designing, constructing, and maintaining the pipelines that allow organizations to collect, process, and analyze massive amounts of data efficiently.
The Role of a Data Engineer
Data engineers are responsible for building the architecture that supports analytics, machine learning, and business intelligence. They develop reliable data pipelines that extract information from various sources, clean and structure it, and make it usable for analysts and decision-makers. Their work ensures that data is accessible, accurate, and available when needed.
Common tasks include:
-
Designing and maintaining data warehouses and lakes
-
Building ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines
-
Integrating APIs and third-party data sources
-
Implementing data quality and governance practices
-
Collaborating with data scientists and analysts
Essential Skills for Data Engineers
To succeed in this role, candidates must combine programming, cloud, and analytical expertise. Key skills include:
-
Programming Languages: Python, SQL, Java, or Scala
-
Cloud Platforms: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
-
Big Data Tools: Apache Spark, Hadoop, and Kafka
-
Database Systems: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Snowflake, Redshift
-
ETL & Workflow Tools: Airflow, dbt, Talend
-
Version Control: Git, CI/CD pipelines
Strong problem-solving skills and a deep understanding of data structures are essential for creating scalable, fault-tolerant data pipelines.
Why Data Engineer Jobs Are in Demand
As companies adopt AI, analytics, and IoT, the need for structured, high-quality data has skyrocketed. Industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, and technology all rely on data engineers to turn raw information into actionable insights. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that data related roles will continue to grow much faster than average over the next decade, making this one of the most secure and rewarding careers in tech.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Data engineers can progress into senior or specialized positions such as:
-
Senior Data Engineer
-
Data Architect
-
Machine Learning Engineer
-
Cloud Data Engineer
-
Analytics Engineer
Many organizations also offer hybrid roles that blend data engineering with DevOps or software development, opening diverse career paths.
Certifications That Boost Your Profile
Earning relevant certifications can make candidates more competitive. Popular ones include:
-
AWS Certified Data Analytics – Specialty
-
Google Professional Data Engineer
-
Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Engineer Associate
-
Databricks Certified Data Engineer
These credentials validate technical expertise and help professionals stand out in a crowded job market.
How to Get Started in Data Engineering
For beginners, the best approach is to start learning Python and SQL, then move on to cloud and big data tools. Building projects on platforms like GitHub or Kaggle also helps showcase real world skills. Networking on LinkedIn and joining online communities can connect you with mentors and job opportunities.
Real-World Impact of Data Engineers
Data engineers drive decisions that shape modern businesses. They enable:
-
Personalized marketing strategies through customer analytics
-
Fraud detection systems in banking and fintech
-
Predictive maintenance in manufacturing
-
Real-time recommendations in e-commerce and streaming platforms
Their work forms the backbone of every data-driven initiative across industries.
Conclusion
The demand for data engineer jobs continues to rise as businesses embrace digital transformation. Skilled professionals who can manage and optimize complex data systems are now at the core of every successful organization.
For companies looking to strengthen their data ecosystem, partnering with expert data engineering consulting services ensures scalability, reliability, and performance—laying the groundwork for smarter, faster business decisions.