Understanding carbon chemistry is essential for anyone exploring the vast world of chemical sciences. As the backbone of organic molecules, carbon plays a central role in everything from life processes to industrial applications.
Building a strong foundation in carbon chemistry not only enhances academic performance but also opens doors to various career paths in medicine, pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and material engineering. To excel in these fields, a thorough grasp of carbon's unique bonding capabilities, structure, and reactions is vital.
Why Carbon Is the Core of Organic Chemistry
Carbon’s significance stems from its versatility. With four valence electrons, carbon can form four covalent bonds with a variety of atoms. This bonding flexibility allows for the formation of a vast array of complex structures such as chains, rings, and frameworks of almost infinite variety. These structures form the basis of organic compounds.
Carbon-carbon bonds are particularly stable, and this stability makes long chains and complex molecules possible. This unique property is crucial in forming polymers, fuels, pharmaceuticals, and even biological molecules like DNA and proteins. Furthermore, the ability of carbon to bond with itself and other elements in multiple ways, including single, double, and triple bonds, makes it exceptionally versatile.
Key Concepts to Master in Carbon Chemistry
To build a strong foundation, it's important to understand several core concepts in carbon chemistry:
1. Hybridization and Molecular Geometry
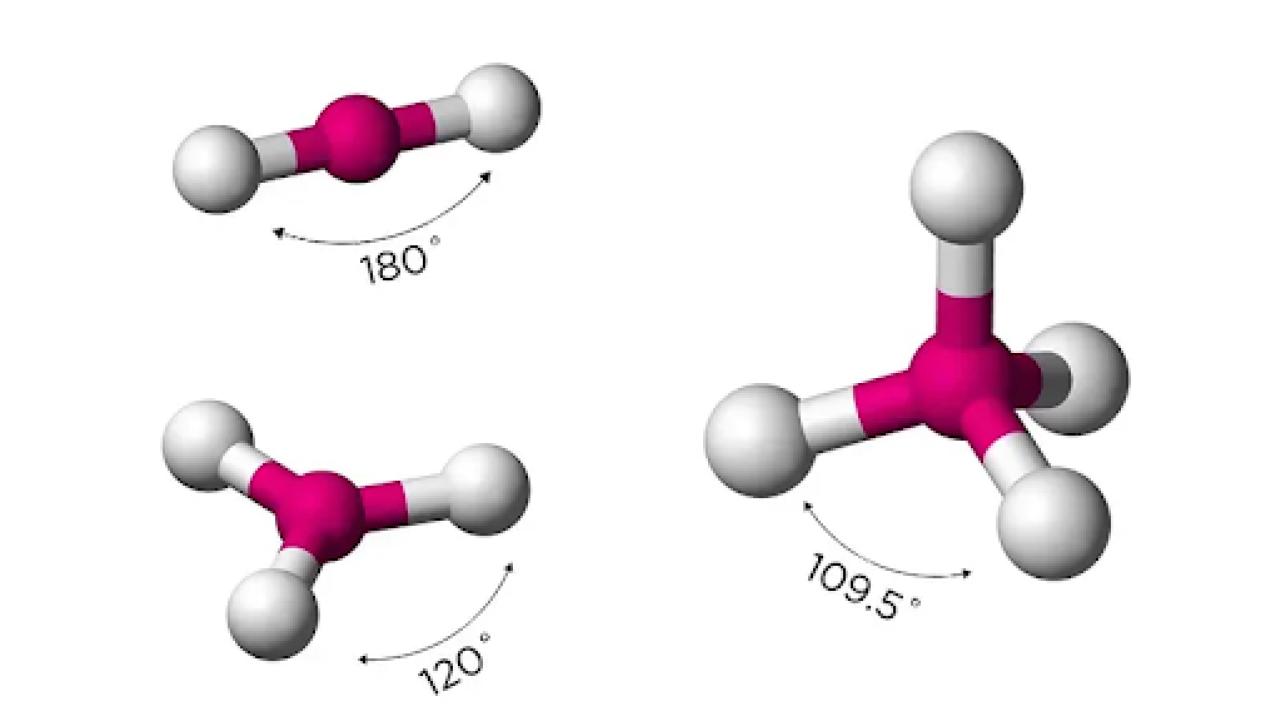
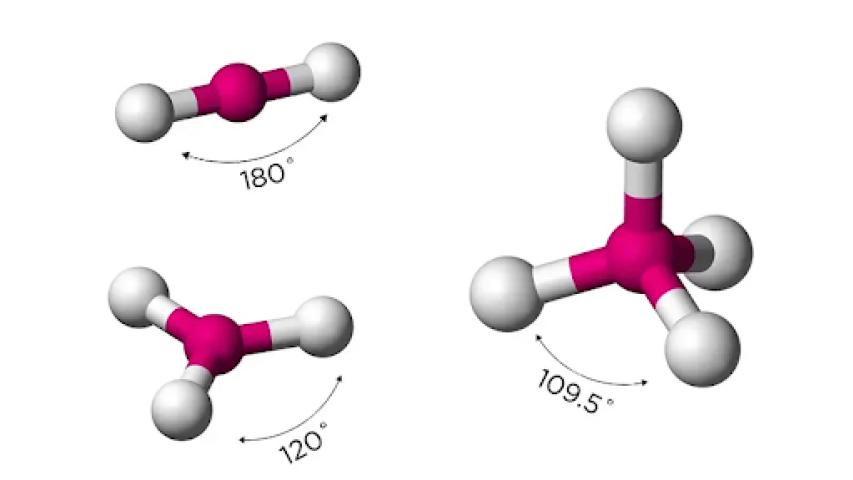
Hybridization explains how carbon’s atomic orbitals mix to form new hybrid orbitals. For example, in methane (CH4), carbon undergoes sp3 hybridization, leading to a tetrahedral molecular geometry. Understanding hybridization helps explain the shapes and angles of organic molecules, which in turn affects their reactivity and physical properties.
2. Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific clusters of atoms within molecules that determine the chemical behavior of those molecules. Learning about alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, amines, and others allows students to predict reactivity and interaction patterns.
3. Isomerism
Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures. Structural isomers differ in connectivity, while stereoisomers differ in spatial orientation. Mastering this topic is essential for understanding how molecular arrangement impacts chemical behavior and biological activity.
4. Reaction Mechanisms
Carbon compounds undergo a wide variety of chemical reactions. Learning reaction mechanisms, the step-by-step processes by which these reactions occur, provides insight into how molecules interact and transform. This includes substitution, elimination, addition, and oxidation-reduction reactions.
How to Approach Learning Carbon Chemistry Effectively
Carbon chemistry can be challenging due to the abstract nature of its concepts and the volume of information. However, with the right approach, anyone can master it.
Visual Learning Tools
Molecular geometry and bonding are best understood visually. Using 3D models, diagrams, or molecular modeling kits helps learners grasp spatial relationships in organic molecules. This is especially useful for understanding stereochemistry and chirality.
Practice Problems and Repetition
Repetition solidifies understanding. Working through various problem sets allows students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical examples. Regular practice with reaction mechanisms, naming conventions, and drawing structures enhances retention.
Structured Learning Resources
Enrolling in a structured organic chemistry online course can provide clear guidance and a step-by-step progression through topics. These courses often offer video tutorials, interactive quizzes, and access to expert instruction, making complex subjects more approachable and easier to understand.
Real-World Applications of Carbon Chemistry
A solid foundation in carbon chemistry isn't just academic, it has practical and impactful applications in many areas of modern life.
Pharmaceuticals and Medicine
Many drugs are organic compounds whose design relies on carbon-based chemistry. Understanding how different functional groups affect biological activity helps in drug development and pharmacology.
Environmental Science
Carbon chemistry is crucial in understanding pollutants, greenhouse gases, and sustainable energy sources. Knowledge of carbon cycles, combustion, and chemical degradation helps address pressing environmental issues.
Industrial and Material Chemistry
From plastics to synthetic fibers, carbon chemistry is at the heart of many manufacturing processes. Innovations in nanotechnology, electronics, and biodegradable materials also stem from manipulating carbon-based molecules.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While carbon chemistry is fascinating, students often face some hurdles along the way:
Abstract Concepts
Some students struggle with visualizing molecules and understanding abstract ideas like resonance or orbital hybridization. Using visualization tools, videos, and guided tutorials can make these topics more accessible.
Memorization vs. Understanding
Rote memorization of reactions and structures without comprehension leads to confusion. It’s more effective to understand the logic behind mechanisms, which makes it easier to predict outcomes and apply knowledge flexibly.
Complex Nomenclature
Naming organic compounds can be overwhelming due to complex rules. Breaking the naming process into smaller steps and consistent practice with examples helps demystify IUPAC naming conventions.
Tips for Building Long-Term Mastery
To retain and build upon your knowledge of carbon chemistry, consider the following strategies:
Teach What You Learn
Explaining concepts to peers or even to yourself reinforces understanding. Teaching helps identify gaps in knowledge and encourages deeper engagement with the material.
Stay Curious and Explore Beyond Textbooks
Carbon chemistry extends far beyond the classroom. Reading scientific articles, watching documentaries, or following industry news can deepen your appreciation and keep your motivation high.
Connect Concepts Across Topics
Recognize the connections between carbon chemistry and other branches of chemistry and science. This interdisciplinary approach strengthens your overall understanding and makes learning more cohesive.
Final Thoughts
Building a strong foundation in carbon chemistry is not just about passing exams, it's about developing the tools and mindset necessary for innovation and problem-solving in various scientific fields. With focused learning, consistent practice, and the right resources, mastering this essential branch of chemistry becomes an achievable and rewarding goal.