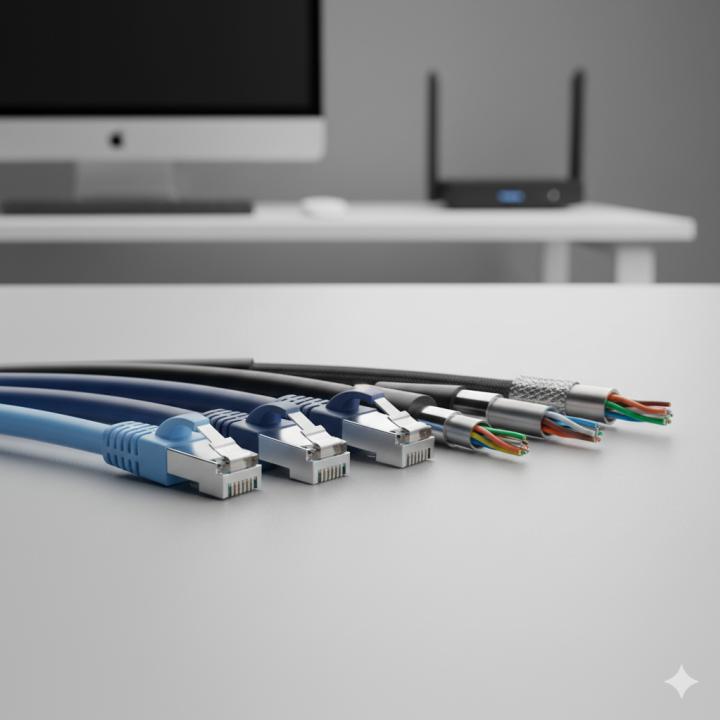
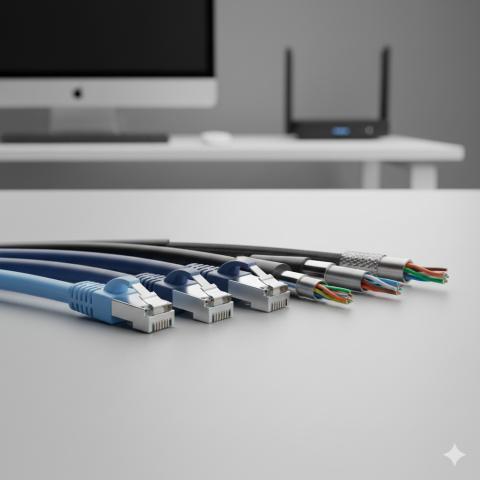
Choosing the right network cable is essential for a fast and reliable internet connection. Cat5, Cat6, Cat7, and Cat8 cables are commonly used in homes, offices, and data centers. Understanding their differences helps you pick the best cable for your needs.
Cat5 cables are the oldest type still in use. They support speeds up to 100 Mbps and frequencies up to 100 MHz. Cat5 cables are suitable for basic internet tasks like browsing, emailing, and streaming standard videos. They are affordable but have limitations in high-speed applications.
Cat6 cables are an upgrade over Cat5. They support speeds up to 1 Gbps and frequencies up to 250 MHz. Cat6 cables also offer better resistance to interference compared to Cat5. They are ideal for gaming, HD video streaming, and small office networks. Cat6 cables are backward compatible with Cat5 devices, making them versatile.
Cat6a is a slightly improved version of Cat6. It can handle speeds up to 10 Gbps at 500 MHz for distances up to 100 meters. The extra shielding reduces crosstalk and interference. For high-speed networks or offices with multiple devices, Cat6a is a reliable choice.
Cat7 cables take network performance further. They support speeds up to 10 Gbps and frequencies up to 600 MHz. Cat7 cables have individual shielding for each pair of wires, reducing interference and providing better signal quality. These cables are suitable for data centers, enterprise networks, and high-speed applications. Cat7 uses GG45 or RJ45 connectors and is backward compatible with Cat6 and Cat5.
Cat8 cables are the newest and fastest standard. They support speeds up to 40 Gbps and frequencies up to 2000 MHz. Cat8 cables are primarily designed for data centers and server rooms where extremely high-speed data transfer is required. They have heavy shielding to prevent interference and maintain signal integrity over shorter distances, typically up to 30 meters.
When comparing Cat5, Cat6, Cat7, and Cat8, the main differences are speed, frequency, shielding, and intended use. Cat5 is suitable for basic networking, Cat6 and Cat6a for faster home or office networks, Cat7 for professional environments, and Cat8 for data centers with high-speed requirements.
Another key difference is shielding. Cat5 cables often have unshielded twisted pairs, which makes them more prone to interference. Cat6 and Cat6a may have some shielding, while Cat7 and Cat8 are fully shielded to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. Shielding ensures stable performance in environments with multiple electronic devices.
Distance limitations are also important. Cat5 and Cat6 can transmit data over 100 meters for standard speeds. Cat6a maintains 10 Gbps over 100 meters, but Cat7 and Cat8 have shorter effective ranges for maximum speeds. Cat8, for example, is ideal for short runs in data centers rather than long home installations.
Cost is another factor to consider. Cat5 cables are the most affordable, followed by Cat6 and Cat6a. Cat7 and Cat8 cables are more expensive due to higher performance and better shielding. Choosing the right cable depends on your network requirements and budget.
Installation is also different for each type. Cat5 and Cat6 cables are flexible and easy to install. Cat7 and Cat8 are thicker and less flexible due to extra shielding, which may require careful handling during installation. Proper cable management ensures optimal performance and prevents damage.
Backward compatibility is an advantage of higher-category cables. Cat6, Cat7, and Cat8 cables can work with older devices that support lower speeds. This makes upgrades easier without replacing all existing equipment. Using a higher-category network cable in a lower-speed system still provides durability and better shielding.
Future-proofing your network is another reason to consider Cat6a, Cat7, or Cat8 cables. As internet speeds continue to increase and more devices connect to networks, higher-performance cables ensure your system can handle future demands without frequent replacements. Investing in better cables now can save costs in the long run.
For home users, Cat5 or Cat6 cables are usually sufficient for streaming, gaming, and regular internet use. Small offices may benefit from Cat6a or Cat7 cables to support multiple users and higher-speed connections. Large enterprises and data centers require Cat7 or Cat8 cables for high-bandwidth operations and reliable performance.
Quality also matters. Not all network cables are made the same. Using certified cables from trusted brands ensures consistent performance and reduces the risk of interference or failure. High-quality network cables last longer and maintain stable connections over time.
When selecting a network cable, consider your speed requirements, distance, environment, budget, and future needs. Cat5 is fine for basic use, Cat6 and Cat6a for faster home or office setups, Cat7 for professional networks, and Cat8 for high-speed data center operations. Properly choosing the cable ensures a reliable and efficient network.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between Cat5, Cat6, Cat7, and Cat8 helps you make an informed choice. Factors like speed, frequency, shielding, distance, installation, and cost play a significant role. Using the right network cable improves performance, reduces interference, and future-proofs your network. Investing in quality cables today ensures stable and fast connections for years to come.
https://sfcable.hashnode.dev/should-i-get-a-cat6-or-7-ethernet-cable