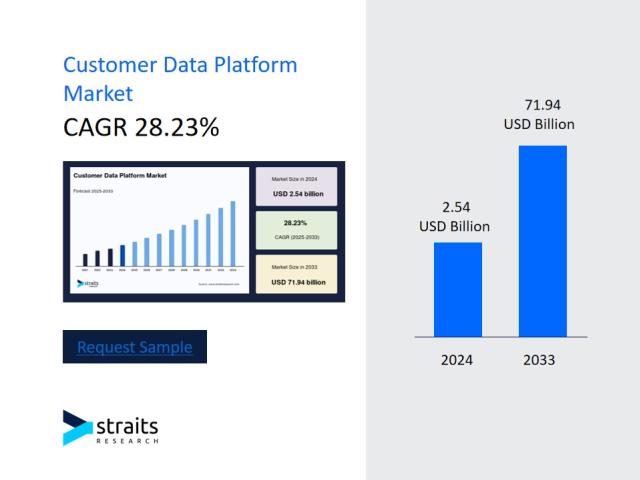
As organizations continue to expand their cloud environments, virtualized workloads, and distributed applications, data center security has become a core priority for IT professionals. Many learners preparing for advanced Cisco certifications begin by strengthening their foundation in CCNP Data Center concepts. Through structured learning paths such as the CCNP Data Center Course, candidates gain the skills required to secure modern data center environments and meet the demands of evolving network architectures.
This article explores the key elements of data center
network security and how they align with CCNP training objectives.
Why Data Center Network Security Matters
Data centers are at the heart of organizational operations,
storing critical information and running mission-essential services. As threats
grow more advanced, security teams must protect:
- Virtualized
workloads
- Multicloud
traffic flows
- Storage
systems and databases
- Application
delivery paths
- Infrastructure
management platforms
CCNP candidates are expected to understand how to secure
these components using both Cisco technologies and industry best practices.
Core Components of Data Center Network Security
1. Segmentation and Micro-Segmentation
Segmentation limits lateral movement by isolating network
areas. In data centers, segmentation is achieved through:
- VLANs
- VRFs
- Micro-segmentation
in solutions like ACI
Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) allows
granular policy enforcement, aligning directly with the security topics covered
in CCNP Data Center learning tracks.
2. Zero-Trust Security Models
Zero-trust principles require verification at every point,
regardless of location. In a data center environment, this means:
- Strict
identity controls
- Least-privilege
access
- Continuous
traffic inspection
- Policy-based
enforcement
Cisco tools like ISE, ACI, and firewalls help implement this
model.
3. Secure Access and Identity Control
Identity-aware security is essential for both internal and
external users. Key components include:
- Role-based
access control (RBAC)
- Multi-factor
authentication
- TACACS+
and RADIUS integration
- Secure
administrative access
These fundamentals are important not only for CCNP
certification but also for securing real-world enterprise infrastructures.
4. Firewalling and Threat Prevention
Firewalls remain a frontline defense mechanism within data
center networks. Cisco firewalls provide:
- Stateful
inspection
- Next-generation
threat detection
- Deep
packet inspection
- Application
visibility and control
Threat prevention solutions like Cisco Secure Firewall and
ACI contracts ensure workloads remain protected from malicious activity.
5. Secure Fabric Policies in Cisco ACI
ACI security is a major topic across CCNP modules. ACI
enforces security through:
- Endpoint
groups (EPGs)
- Contracts
controlling allowed traffic
- Filters
applied to specific protocols
- Policy-driven
isolation
This allows administrators to secure applications based on
intent rather than manual configuration.
6. Data Encryption and Secure Communication
Protecting data in motion is critical. Techniques include:
- MACsec
for Layer 2 traffic
- IPsec
tunnels for inter-site communication
- TLS
and SSL for application-level encryption
Encryption ensures confidentiality even when traffic moves
across untrusted networks.
7. Monitoring, Analytics, and Telemetry
Security isn’t just about prevention—it also requires
visibility. Cisco provides telemetry and analytics tools that help detect
anomalies early.
Important features include:
- NetFlow
and sFlow
- ACI
health scores
- Real-time
fabric monitoring
- Syslogs
and SNMP
CCNP candidates must understand how to interpret these tools
to strengthen incident response.
How CCNP Training Helps Build These Skills
The CCNP Data Center Course aligns with industry
expectations by teaching candidates how to:
- Secure
physical, virtual, and cloud-based infrastructures
- Configure
ACI policy models
- Implement
identity and access controls
- Troubleshoot
security issues within data center fabrics
- Build
scalable, secure topologies
Practical labs and theoretical modules ensure students
develop both understanding and hands-on experience.
Common Challenges Learners Face
Many CCNP candidates initially struggle with:
- Understanding
ACI security contracts
- Mapping
business requirements to policy models
- Troubleshooting
encrypted traffic
- Visualizing
segmentation strategies
Overcoming these challenges requires consistent lab practice
and reviewing official Cisco documentation.
Best Practices for Data Center Network Security
To stay aligned with global standards, engineers should:
- Update
policies regularly
- Use
multi-layer security controls
- Monitor
network health continuously
- Keep
firmware and security signatures up-to-date
- Automate
repetitive security tasks where possible
Following these practices helps create resilient, compliant,
and scalable data center environments.
Conclusion
Data center network security is a crucial skillset for IT
professionals pursuing advanced Cisco certifications. By understanding
segmentation, identity management, ACI policies, firewalls, and encryption,
learners can protect modern enterprises against increasingly sophisticated
threats. Structured programs like the CCNP Data Center Course and the
broader CCNP Data Center certification path help professionals build
these capabilities and advance in their careers.