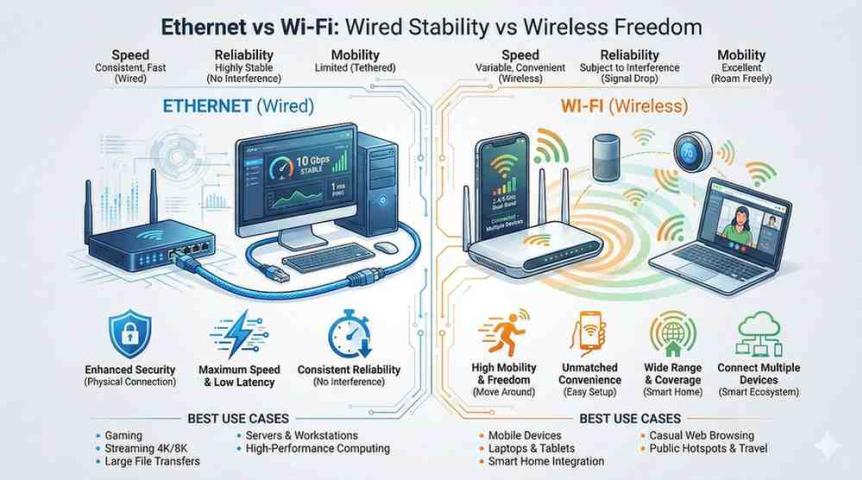
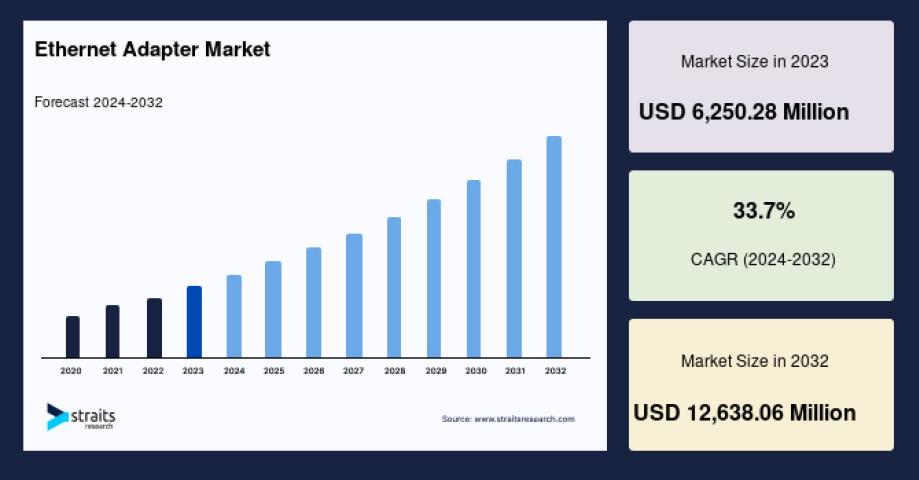
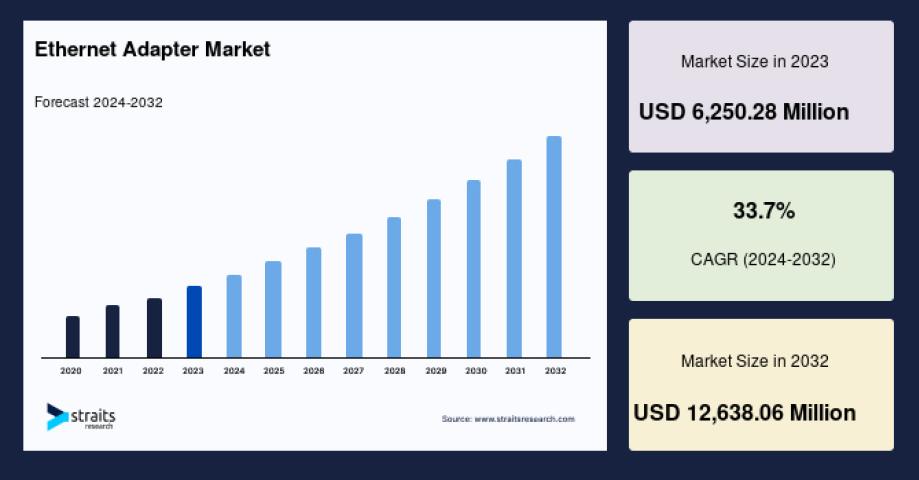
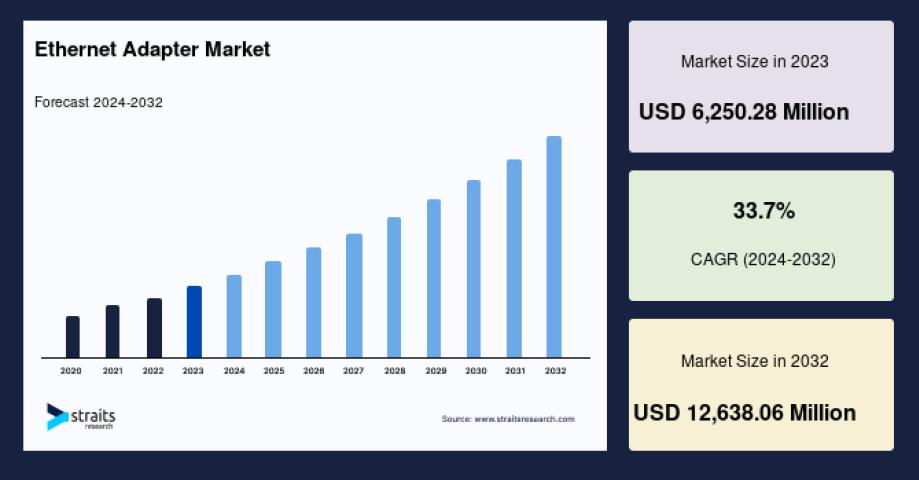
When you're setting up a home network, upgrading your office infrastructure, or building a data center, choosing the right ethernet cable can make a significant difference in your network's performance. The market offers several categories of ethernet cables, each designed for specific speed requirements and applications. Understanding the differences between Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8 cables will help you make an informed decision that matches your current needs and future requirements.
Understanding Ethernet Cable Categories
Ethernet cable categories represent standardized specifications that define a cable's performance capabilities. Each category provides specific maximum speeds, bandwidth frequencies, and transmission distances. As technology advances, newer categories emerge to support faster data transfer rates and more demanding applications.
The "Cat" designation stands for "category," and the number or alphanumeric combination indicates the generation and capability level. Higher numbers generally mean better performance, but they also come with increased costs and installation considerations.
Cat5e: The Reliable Workhorse
Cat5e, or Category 5 enhanced, represents an improved version of the original Cat5 standard. This ethernet cable became the baseline for modern networking and remains widely used today.
Performance Specifications
Cat5e cables support speeds up to 1 Gbps (Gigabit per second) over distances up to 100 meters. They operate at frequencies up to 100 MHz, which provides sufficient bandwidth for most home and small office applications. The cable uses twisted pair construction with four pairs of copper wires to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Best Use Cases
Cat5e works perfectly for basic internet browsing, streaming video content, online gaming, and standard office applications. Most residential internet connections don't exceed 1 Gbps, making Cat5e an economical and practical choice. Small businesses with moderate networking demands also benefit from its cost-effectiveness and reliable performance.
Cat6: Enhanced Speed and Reduced Interference
Category 6 cables represent a significant upgrade over Cat5e technology. Manufacturers introduced this ethernet cable standard to support faster speeds and provide better protection against crosstalk.
Performance Specifications
Cat6 cables deliver speeds up to 10 Gbps, though this maximum speed applies only to cable runs up to 55 meters. For distances between 55 and 100 meters, Cat6 supports speeds up to 1 Gbps. The frequency rating reaches 250 MHz, offering more than double the bandwidth of Cat5e.
The cable features tighter twisting of wire pairs and often includes a plastic spline that separates the pairs, reducing crosstalk and electromagnetic interference.
Best Use Cases
Cat6 suits environments where you need higher speeds for data-intensive applications. Video editing studios, medium-sized businesses, and tech-forward homes benefit from Cat6's improved performance. The cable provides excellent future-proofing for networks that may upgrade to faster internet services or implement 10 Gbps local area networks.
Cat6a: Augmented Performance for Demanding Applications
Category 6 augmented (Cat6a) extends the capabilities of Cat6 technology. This ethernet cable eliminates the distance limitation that restricts Cat6's 10 Gbps performance.
Performance Specifications
Cat6a maintains 10 Gbps speeds across the full 100-meter distance. The frequency rating doubles to 500 MHz, providing substantial bandwidth for demanding applications. Cat6a cables typically feature thicker construction and improved shielding, which eliminates alien crosstalk—interference between adjacent cables.
Best Use Cases
Data centers, hospitals, educational institutions, and enterprises with high-bandwidth requirements rely on Cat6a infrastructure. The cable supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications effectively, making it ideal for networks that power security cameras, wireless access points, and VoIP phones. Organizations planning long-term network investments choose Cat6a for its robust performance and future compatibility.
Cat7: Professional-Grade Shielding
Category 7 cables introduce comprehensive shielding that sets them apart from previous standards. Each wire pair receives individual shielding, and an additional outer shield protects the entire cable bundle.
Performance Specifications
Cat7 supports frequencies up to 600 MHz and maintains 10 Gbps speeds across 100 meters. Some implementations can achieve speeds up to 40 Gbps over shorter distances. The extensive shielding virtually eliminates electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, ensuring signal integrity in challenging environments.
Best Use Cases
High-interference environments, such as factories with heavy machinery or facilities with extensive electrical equipment, benefit from Cat7's superior shielding. Professional recording studios and broadcasting facilities use Cat7 to maintain pristine signal quality. However, Cat7 cables require specialized GG45 or TERA connectors rather than standard RJ45 connectors, which can complicate installation and increase costs.
Cat8: The Cutting Edge of Ethernet Technology
Category 8 represents the latest ethernet cable standard, designed specifically for data center applications and high-performance computing environments.
Performance Specifications
Cat8 delivers unprecedented speeds of 25 Gbps or 40 Gbps, depending on the specific standard (Cat8.1 or Cat8.2). The frequency rating reaches an impressive 2000 MHz, though the maximum transmission distance shortens to 30 meters. Like Cat7, Cat8 features comprehensive shielding on individual pairs and the entire cable assembly.
Best Use Cases
Data centers requiring ultra-fast server-to-switch connections deploy Cat8 infrastructure. High-frequency trading operations, cloud service providers, and research institutions with massive data processing needs utilize Cat8's extreme performance capabilities. The limited distance range makes Cat8 impractical for most standard networking applications, but perfect for specialized, high-density computing environments.
Making Your Selection
Choosing the right ethernet cable depends on your specific requirements, budget, and future plans. Cat5e remains sufficient for basic home networking, while Cat6 provides excellent value for future-proofing residential and small business installations. Cat6a serves demanding business environments well, and Cat7 or Cat8 fulfill specialized professional requirements.
Consider your maximum required speeds, cable run distances, environmental interference factors, and budget constraints. Remember that installing higher-category cables during initial construction costs less than upgrading later, making modest over-specification often worthwhile for long-term network investments.
Source: https://www.iplocation.net/different-ethernet-cables-with-their-features-and-applications